Psychologist Rosa Hidalgo explains in this article what hippotherapy is, what its bases are, its main benefits and how the intervention with horses is carried out.
What is hippotherapy?
The name hippotherapy comes from the Greek hippos (horse) and therapeia (treatment). It is a specialty of Kinesiotherapy (the science that studies movement, anatomy and physiology of the biomechanics of the body) where the therapeutic effects of the horse are combined with specific kinesiological exercises according to the patient’s diagnosis. Hippotherapy is, therefore, a rehabilitation treatment.
In its beginnings, in the 1950s-1960s, hippotherapy was used to treat patients in the fields of orthopedics and neurology. Through experience and research, from the 1990s it expanded to areas such as psychiatry, pedagogy, speech therapy, and genetic diseases. Currently, other health professionals also practice hippotherapy such as physicians, psychologists, and occupational therapists.
Who is hippotherapy intended for?
It is indicated for the following clinical conditions:
Cerebral palsy, ataxias, spinal cord injuries, brain injuries, spina bifida, muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, Down syndrome, paraplegia, hemiplegia, attention and concentration problems, psychosomatic illnesses, anorexia nervosa, autism, Rett syndrome, fibromyalgia, developmental disorders, psychomotor delay, children who have suffered domestic violence or abandonment, phobias, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder.
What are the foundations of hippotherapy?
Hippotherapy is based on a set of rehabilitative techniques applicable to a large number of disabling conditions. It is based on the transfer of the horse’s movement to the patient. Physical movement, affective bonds and contact with nature are a fundamental aspect of human life and basic elements of hippotherapy.
Cognitive processes such as attention (sustained, selective, alternating), and language are highly effective in hippotherapy, given the bond between the patient and the horse.
Motivation and the affective-emotional relationship play a fundamental role: the patient’s desire to communicate with the animal is so strong that they make an effort to understand it; it is an invitation to participate in activities together.
Other neurological processes that are highly benefited by hippotherapy are memory, the vestibular system, proprioception and motor coordination, both fine and gross.
Basic principles
- Transmission of a three-dimensional locomotion pattern equivalent to the physiological pattern of human gait. The horse’s gait emits a three-dimensional pattern anterior-posterior (top-bottom), cranio-caudal (forward and backward) and latero-medial (side-to-side).
- Transmission of rhythmic impulses. These rhythmic impulses are transmitted to the pelvic girdle, the spine and the rider’s lower limbs, causing reactions of balance and trunk straightening in the patient.
- Heat transfer. The horse’s normal temperature is (38.5 °C). This heat transfer warms the muscles, relaxes them, increases blood flow and stimulates the patient’s tactile sensory perception.
Benefits of hippotherapy
- Improves general physical condition,
- stimulates the sensorimotor system,
- improves coordination, reflexes and motor planning,
- regulates muscle tone: relaxes and strengthens,
- activates internal organs and the heart,
- corrects behavioral problems,
- reduces anxiety,
- promotes concentration and self-esteem,
- acquisition of cognitive and social skills.
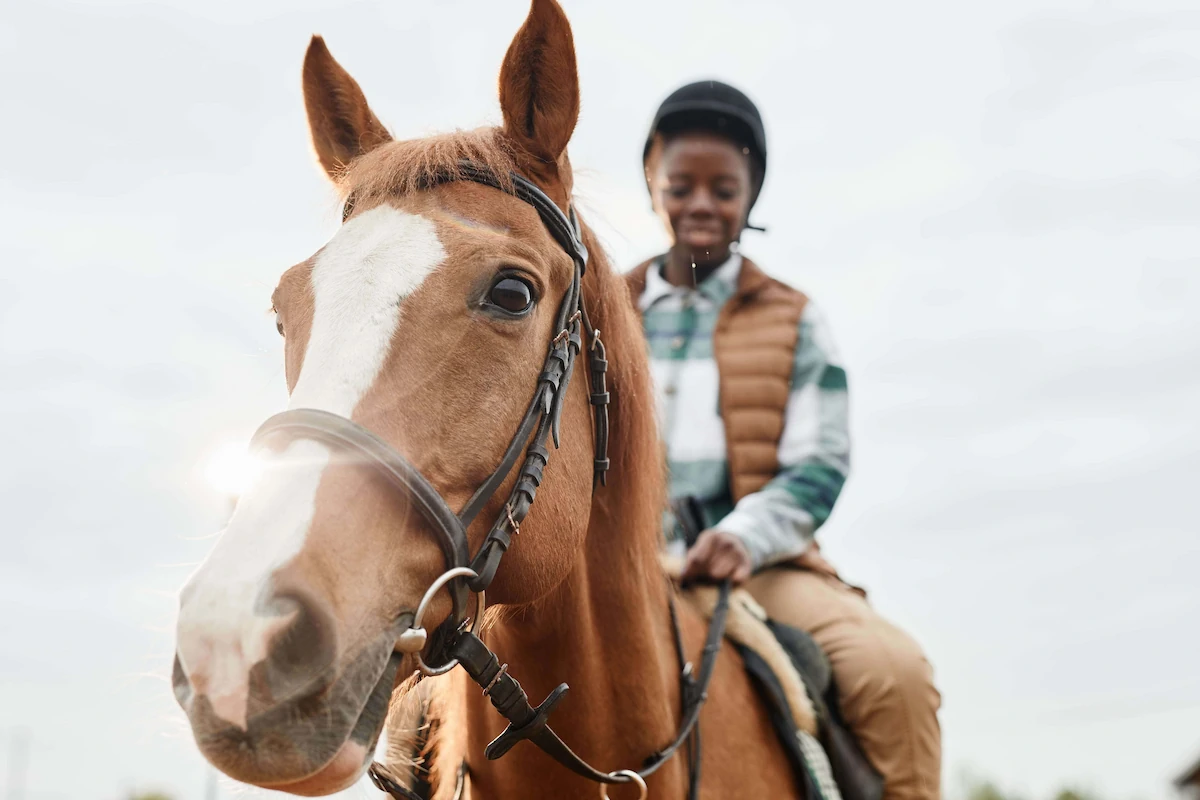

When is hippotherapy contraindicated?
- Uncontrolled epilepsy.
- Extreme hypotonia.
- Intracranial pressure.
- Complete spinal cord injuries, since it is impossible to keep the patient on the horse.
- Insurmountable fear of the horse or of the therapy.
- Presence of dizziness or vertigo.
- Excessive aggressiveness, as it would put the patient in danger due to possible reactions of the horse.
- Atlanto-axial instability in Down syndrome.
How are hippotherapy sessions conducted?
Hippotherapy sessions have a duration of thirty minutes. At the beginning they should be ten or fifteen minutes and gradually extended.
Sessions divided into phases
1º On the ground
At the start of hippotherapy treatment, the patient must gain confidence with the horse and adapt to the environment, which is why the on-ground phase is worked. It is the first phase of the session.
The affective-emotional bond is worked on through horse care and cognitive processes, such as performing a slow and calm brushing to work on impulsivity.
Example activities for the On-ground phase:
| ACTIVITY | OBJECTIVE |
| Greet the horse | Create an affective bond. First approach to the horse, the patient is taught the correct way to approach it and the necessary safety measures. |
| Body schema | Create empathy between the patient and the horse; bodily similarities between the horse and the patient are sought. |
| Farewell to the horse | The horse is taken to the stall and given a reward (carrot). |
2º Mounting
In the second phase, the mounting, most of the therapeutic activities are carried out through exercises and games.
It will always be attempted that the patient performs the autonomous mount (the patient can get on the horse alone). However, there are a series of criteria in which a tandem mount should be performed (the therapist mounts the horse with the patient), and these are when the patient has no trunk control, no head control or the patient appears somewhat insecure.
At the end of the session the patient is rewarded with congratulations from the therapist and family members, since it is important to value the efforts and achievements made.
How is the therapy established?
Clear objectives and guidelines must be set so that the therapy is a progressive process. It is advisable to carry out a evaluation of the patient’s health status both on the ground and on the horse.
The evaluation must consider the diagnosis, clinical history, treatments received, the drugs currently consumed and the kinesiological assessment (gait, seated position, head and trunk control, turns, muscle strength, joint limitations, balance reactions and spinal deviations).
The neurological evaluation includes the detection of symptoms such as paresis, paralysis, muscle tone, pathological reflexes, patterns of abnormal postures and movements.
Regarding cognitive status, attention should be paid to connection with the environment, comprehension, memory, attention and concentration.
Evaluation and follow-up of hippotherapy
After considering the patient’s characteristics, the interdisciplinary team will establish a timeline, where it will evaluate the progress of the therapy, adapting the sessions according to each person’s needs.
Conclusions
Several studies agree that hippotherapy improves the patient’s quality of life; it is a therapy that has psychological and social benefits. The reason is that the horse, through its gait pattern, generates vibrations that are transmitted to the spinal cord, so the brain receives the same stimuli as if it were walking.
On the other hand, when a bond with the horse is established, interaction patterns are formed.
It is important to emphasize that hippotherapy is a complementary method, and it is always important to seek good professionals who are properly qualified to carry out the therapy.
Bibliography
- Berneche García, M. E. (2015). Therapies assisted by horses (TAH): The art of rehabilitation at the walk and the role of the psychologist: Equine therapy. Available at: https://www.colibri.udelar.edu.uy/jspui/bitstream/20.500.12008/5817/1/Berneche%2c%20Ma.%20Eugenia.pdf
- Bender R(2018) Hippotherapy. The horse in rehabilitation.IISBN978-956-14-2316-9 (pp16- 428) Editorial: Ediciones UC.
- Bouzo-González, S., & Pino-Juste, M. R. (2015). Impact of a therapeutic riding program on the improvement of psychomotricity in autistic children. Revista de estudios e investigación en psicología y educación, 080-084. Available at: https://revistas.udc.es/index.php/reipe/article/view/reipe.2015.0.11.513/pdf_315
- Cardo, M., & Brasesco, M. V. (2011). The child and the horse from a psychological perspective. Psychology and Psychopedagogy. Available at: https://racimo.usal.edu.ar/4507/1/180-737-1- PB.pdf
- Cañadas Guerreros, C(2018)Equinoterapia. Therapies assisted with horses.(pp-11- 400)Editorial: Paidotribo.
- Eraud A(2020), A proposal for a equine therapy intervention for children with ADHD from an animal protection perspective. Derecho Animal (Forum of Animal Law Studies) 11/2 (2020)DOI https://doi.org/10.5565/rev/da.495
More references
- Cuervo, P. (2017). Benefits of equine therapy in children with ASD. Faculty of Education. University of Cantabria. Available at: https://repositorio.unican.es/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10902/11839/PrietaCuervoJaz minaDeLa.pdf?sequence=1.
- De la Barrera, M. L. (2020). PHYSICAL, PSYCHOLOGICAL AND SOCIAL BENEFITS OF THERAPIES ASSISTED WITH HORSES. A look from Neurodevelopment. (Doctoral dissertation, Faculty of Human Sciences, National University of Río Cuarto) Revista de Equinoterapia. Available at: http://ecrinterapias.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/EVIDENCIA-CIENT%C3%8DFICA-Psico-Neuropsico-y-equit.pdf
- Martos Montes, R., Ordóñez Pérez, D., De la fuente Hidalgo, I., & Martos Luque, R. i. (2015). Animal-assisted intervention (AAI): Analysis of the situation in Spain. Escritos de Psicologia – Psychological Writings (online), 1- 10. Available at: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=271043400001
- Pérez, L., Rodríguez, J. and Rodríguez, N. (2008). Equine therapy in the treatment of childhood disability. AM C [online], 12. Available at: http:https://neuronup.us scielo.sl d.cu/p df/amc /v12n 1/amc1 6108.pdf
- Perez,Ortiz,G, Nelida Avecilla Ramirez, Gl, Calderón Carrillo, M(I2018) Psychological intervention with equine therapy in children with ADHD. Revista NTHE, 23: 44-48, 2018ISSN: 2007- 9079. Available at: http://www.nthe.concyteq.edu.mx/
- Rándolph Delgado Fernández, Belkis Sánchez Gomez.(2015)Influence of equine therapy in the treatment of autistic children aged 5 to 7 years. Mediciego;Vol.21.N.3.ISSN:1029- 3035/RNPS:1821. Available at: http://www.revmediciego.sld.cu/index.php/mediciego/article/view/454/869
If you enjoyed this post about the hippotherapy, you might be interested in these publications from NeuronUP:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
Hipoterapia: qué es, fundamentos, beneficios y metodología




 Autism and the Brain: Neurobiological Causes of Autism
Autism and the Brain: Neurobiological Causes of Autism
Leave a Reply