On the occasion of World Mental Health Day, in this article we explore how neurorehabilitation not only plays a key role in the recovery of cognitive functions but also in improving mental health, highlighting how a comprehensive approach can be key to enhancing patients’ emotional well-being.
Neurorehabilitation and mental health are two areas that are intrinsically related. Cognitive impairments not only affect a person’s ability to perform everyday activities but also influence their emotional well-being.
Understanding mental health
Mental health is much more than the absence of psychological disorders. It is an ongoing process influenced by a series of internal and external factors such as emotional skills, substance use, genetics, social environment and environmental circumstances, among others. Each person faces these experiences in a unique way and, depending on their abilities to manage them, they may experience different levels of emotional stress, distress and unfavorable clinical outcomes.
Maintaining good mental health goes beyond not having mental illnesses; it requires achieving a balance between our thoughts, emotions and behaviors.
The deterioration of mental health ends up affecting not only people’s social capacity but also other areas such as work and even physical health itself, favoring the appearance of diseases that, in some cases, can become chronic.
Therefore, taking care of our mental health is as essential as taking care of our body, since it is a fundamental pillar of our overall well-being.
Neurorehabilitation in mental health
What neurorehabilitation is about
Neurorehabilitation is a set of interventions designed to help people who have suffered damage to the nervous system, such as a stroke (CVA), traumatic brain injuries, neurodegenerative diseases or even a mental disorder. It is a key discipline in the recovery of cognitive functions, motor and sensory functions, restoring the patient’s independence and improving their quality of life.
However, the effect of neurorehabilitation on mental health is often underestimated. Its impact goes beyond improvements in areas such as memory, attention or language. The connection between cognitive function and emotional well-being is deeper than many believe.
When a person experiences a decline in their cognitive abilities, they may face a series of emotional challenges, such as frustration, low self-esteem, anxiety and, in many cases, depression. In this context, neurorehabilitation not only contributes to recovering cognitive skills but also plays a fundamental role in improving mental and emotional health.
Neurorehabilitation and mental health: two interrelated areas
The impact of the loss of cognitive functions goes beyond the mere inability to perform tasks. Patients who suffer these limitations often face feelings of frustration, anxiety, low self-esteem and, in many cases, depression. These emotional symptoms can be as disabling as the cognitive difficulties themselves.

Subscribe
to our
Newsletter
Positive impact of neurorehabilitation on mental health
The impact of cognitive rehabilitation on the recovery of self-esteem
One of the areas in which neurorehabilitation has the greatest impact is the patient’s self-esteem. People who have suffered brain damage or have a condition that affects their cognitive functions, such as memory or planning ability, often experience a loss of control over their daily life. When tasks that were once simple become challenging—such as remembering important details, having difficulty planning tasks or carrying out everyday activities—it is common for self-esteem to decrease significantly and for their mental health to be affected.
In these cases, cognitive rehabilitation focuses on improving these cognitive functions, providing people with the necessary tools to recover the skills they had lost.
This sense of recovery and progress not only grants them greater independence but also:
- generates a favorable attitude toward the recovery process,
- reinforces their positive self-perception,
- reduces their levels of stress and anxiety,
- strengthens their resilience,
- gives them greater autonomy to make decisions and carry out everyday tasks,
- and reconnects them with hobbies, passions and personal projects they had set aside due to their cognitive difficulties.
The importance of planning and flexibility in reducing stress and anxiety
The executive functions, such as planning, flexibility and decision-making, are cognitive areas that not only influence daily performance but are also closely linked to emotional management. When a person loses the ability to organize their thoughts, prioritize tasks or devise alternatives in life situations, it is common for them to experience high levels of stress and anxiety.
Cognitive rehabilitation focuses on restoring these cognitive functions through specific programs. As these improve, the individual feels they are regaining control over their environment, which considerably reduces their levels of stress and anxiety associated with the inability to manage everyday tasks effectively, as well as more complex situations.
Promoting social interaction for emotional well-being
Cognitive functions are also crucial in the development of social skills, especially areas like memory and language. When a patient experiences difficulties in these areas, it is common for them to experience increased social isolation, which can heighten feelings of loneliness and worsen their mental health.
By focusing on improving memory and language, neurorehabilitation enables people to:
- recover their ability to interact more effectively with friends, family and colleagues, facilitating social integration, reducing the feeling of loneliness and improving their mental health.
- make social interactions more fluid and positive, reinforcing social well-being and creating a dynamic in which they feel more connected and supported by their surroundings.
Neurorehabilitation activities for mental health
Attention and memory activities to reduce stress
Improving short- and long-term memory through simple exercises reduces the anxiety associated with forgetting and the lack of control.
1. Remember the Names (audio)
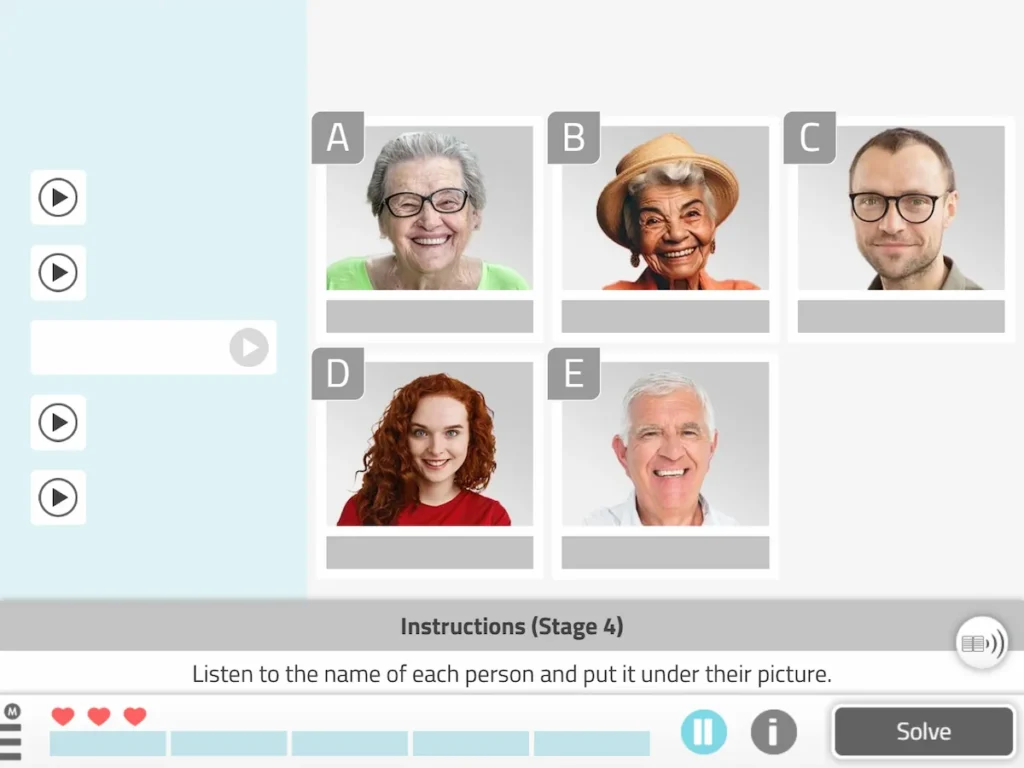
This customizable NeuronUP game for episodic memory consists of listening to, memorizing and matching the names of the people who appear on the screen.
2. Press Conference
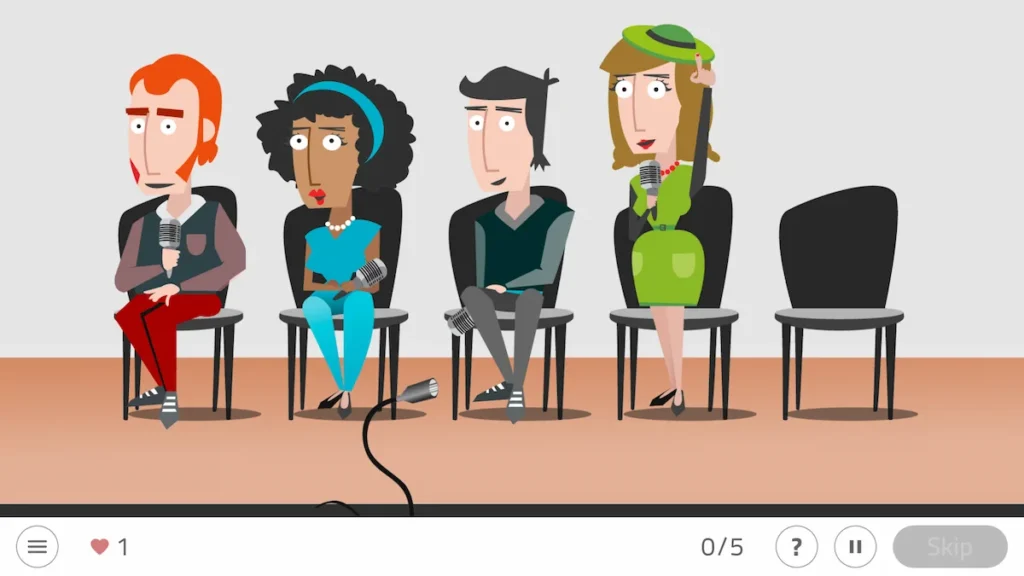

This NeuronUP game consists of remembering the order in which the journalists on the screen requested their turn to speak and then reproducing it.
With this customizable activity, users have the opportunity to work on episodic memory and working memory.
3. Select items from a category
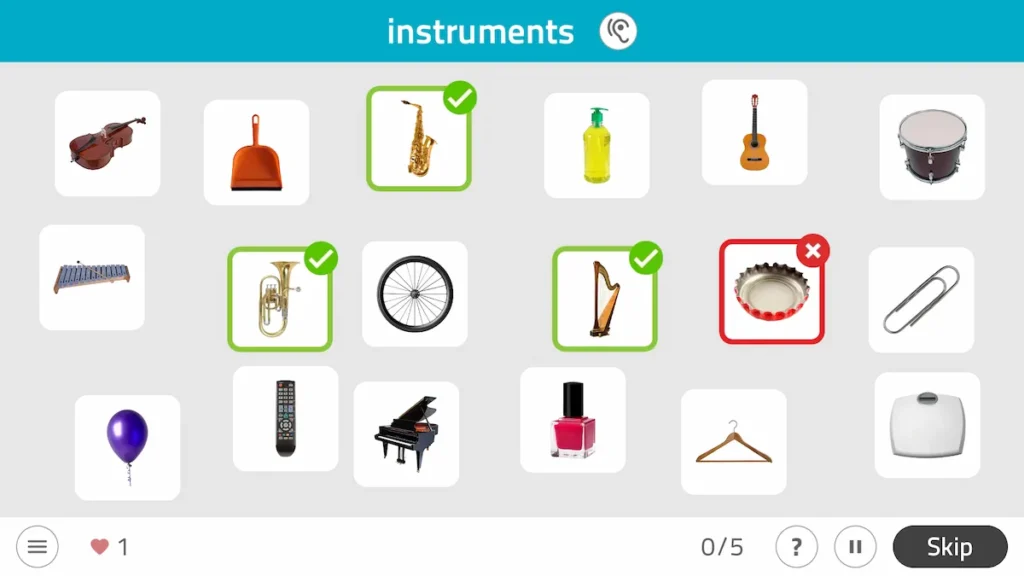
This NeuronUP worksheet for working on selective attention and semantic memory consists of selecting a series of specific items from a group of stimuli.
Executive function activities to improve emotional control
Activities that require organization, planning and cognitive flexibility help strengthen executive functions, which increases the ability to manage complex emotions and stressful situations.
1. Organizing a timetable
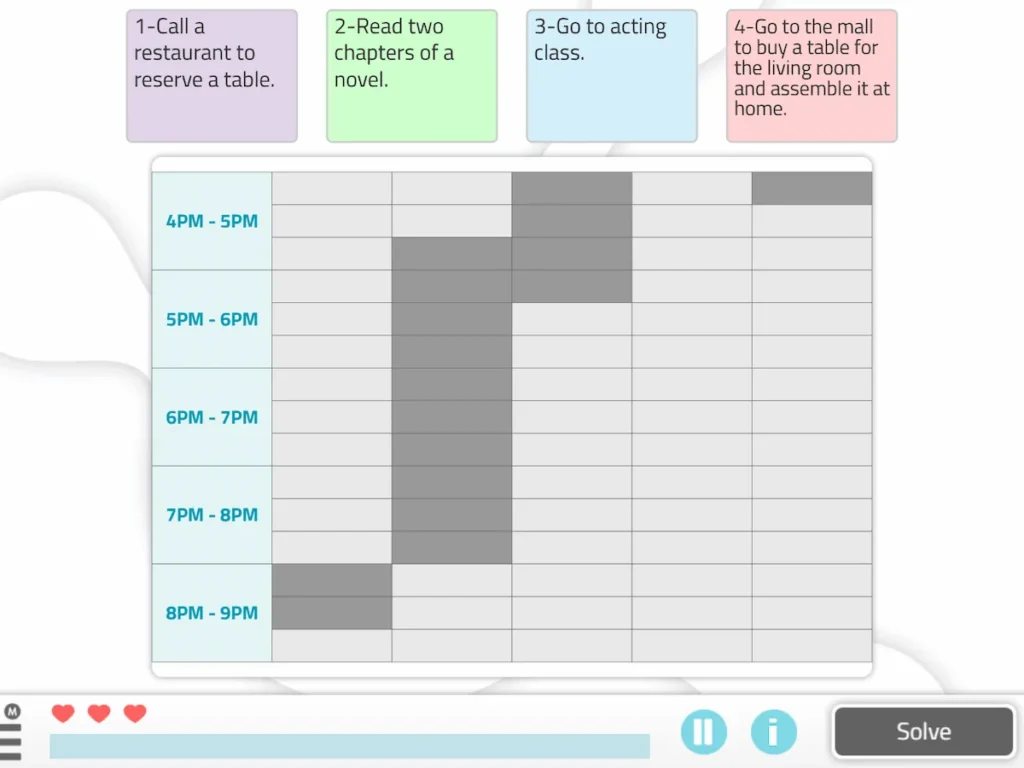
This NeuronUP worksheet for working on planning and time estimation consists of organizing various tasks in a schedule based on the available time.
2. Task sequencing (text-only)
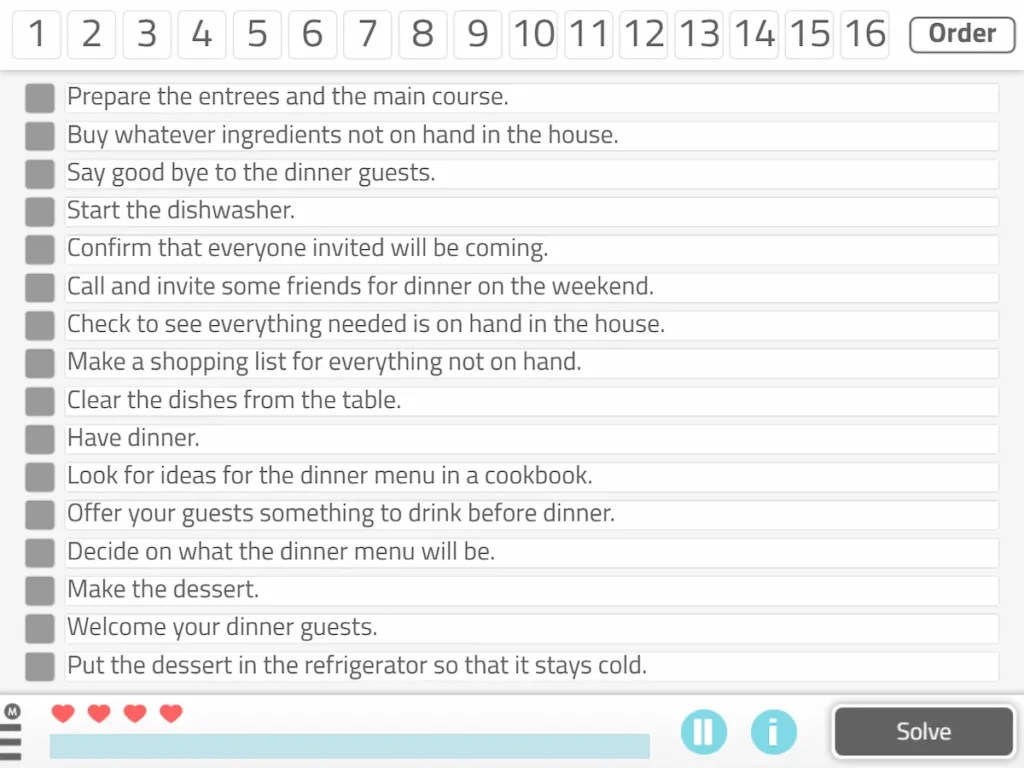
This NeuronUP worksheet consists of ordering the necessary steps to carry out an activity.
With this activity, users have the opportunity to work on their planning, reasoning and comprehension.
3. Varied combinations
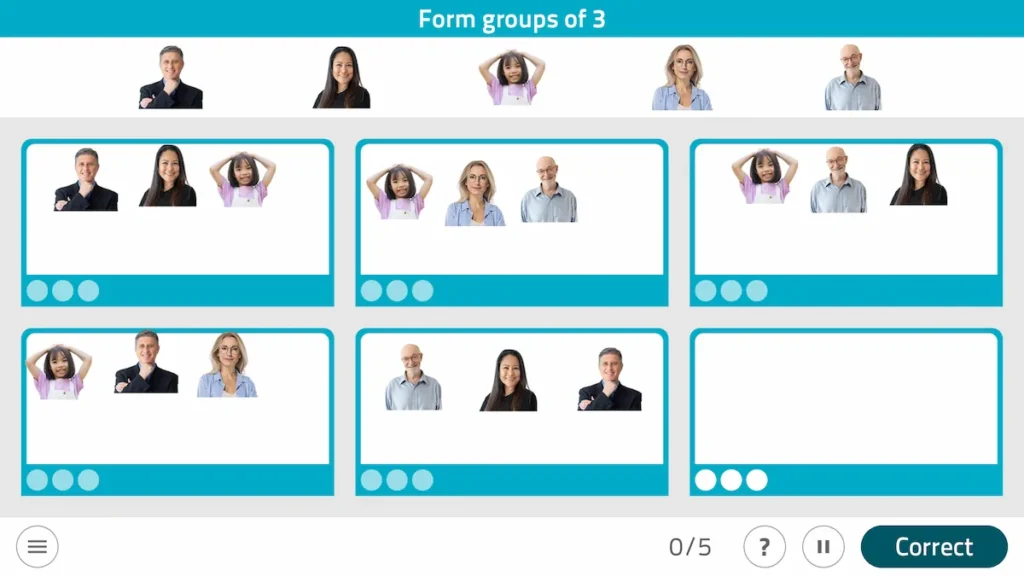
This customizable NeuronUP game, focused on working flexibility and planning, consists of organizing various elements into different groups.
Language activities to improve self-esteem
Improvements in language are fundamental for people to relate in society, communicate their needs and thoughts, and understand others.
1. Form sentences
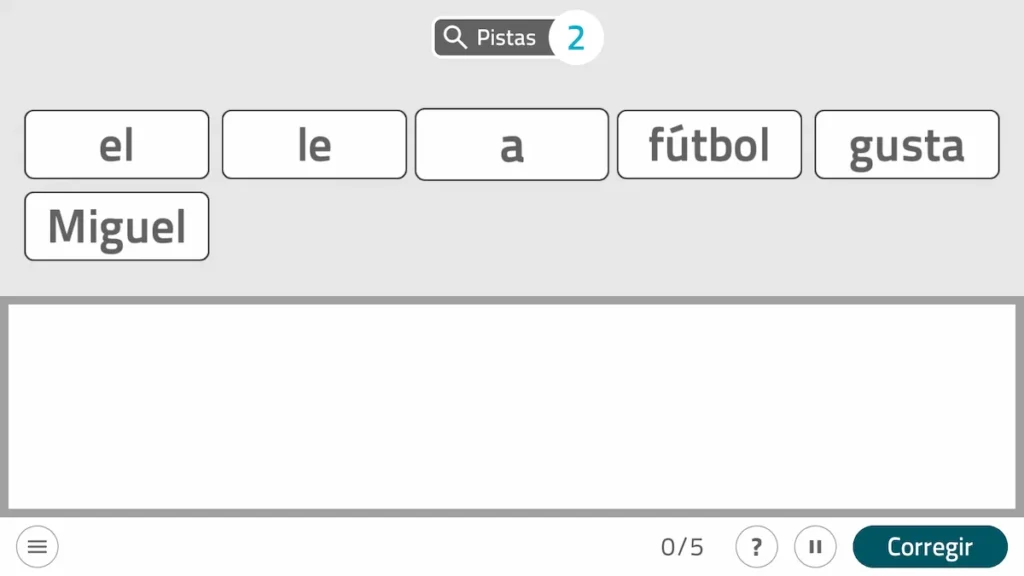
This customizable NeuronUP game consists of ordering the presented words to form coherent syntactic structures.
With this activity, users can improve their expression, working memory, flexibility, planning and comprehension.
2. Differentiate numbers
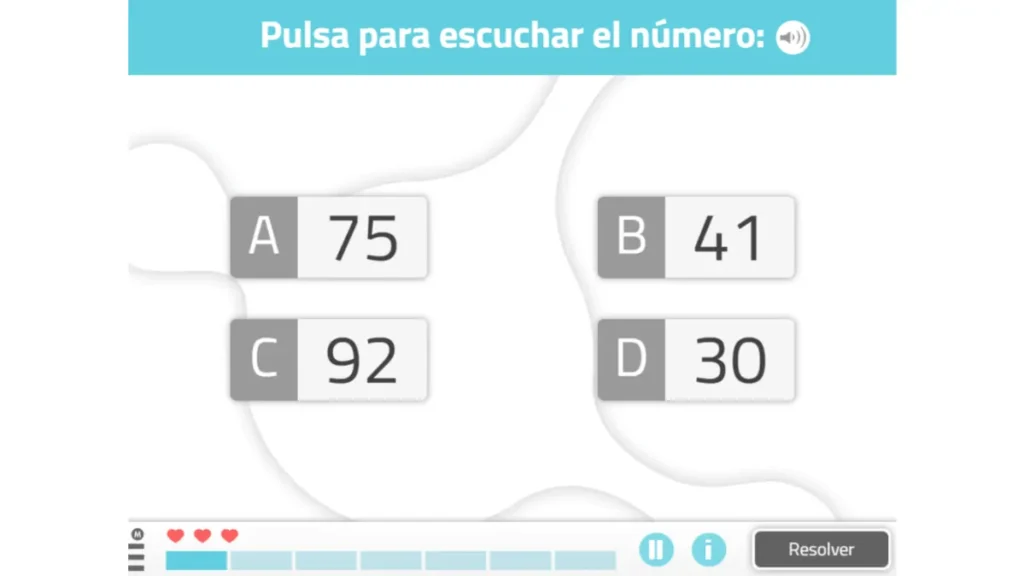
This NeuronUP worksheet for working on discrimination consists of choosing the dictated number among several options.
3. Matching Adjectives to Images
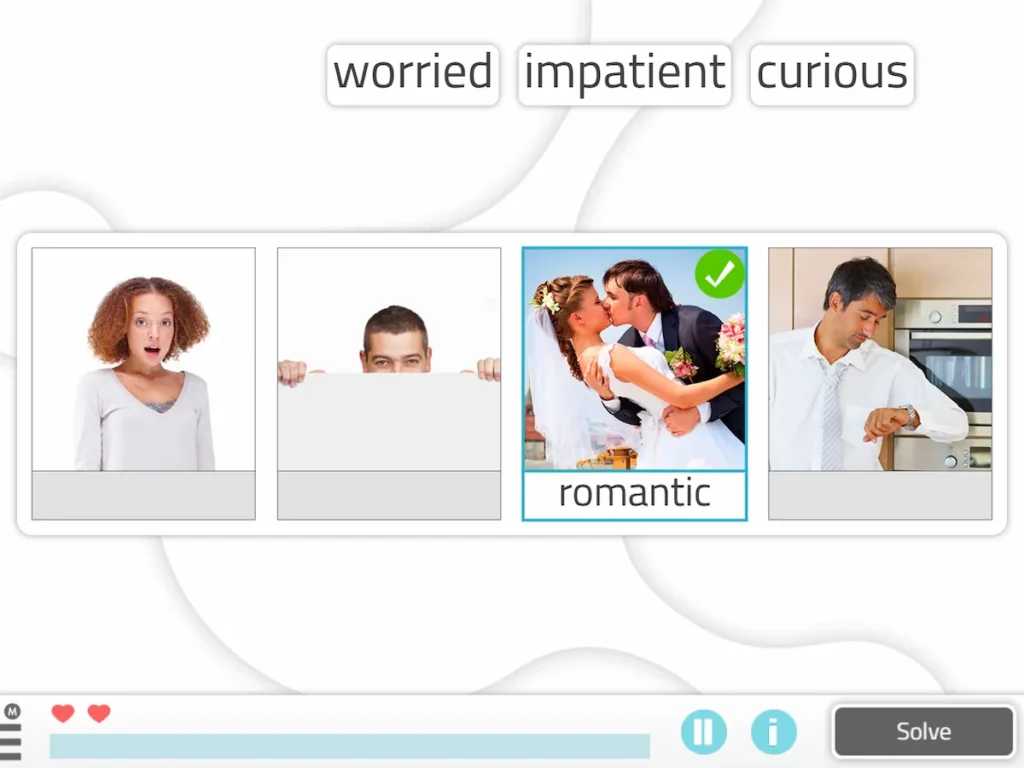
This NeuronUP worksheet for working on vocabulary consists of matching each adjective with the image that represents that characteristic.
Conclusion
Neurorehabilitation not only focuses on restoring affected cognitive functions but also has a significant impact on patients’ mental health. Through improvements in self-esteem, the reduction of stress and anxiety, and the enhancement of social skills, patients experience a comprehensive recovery that encompasses both their cognitive and emotional well-being.
While the recovery of cognitive functions is crucial, emotional well-being is equally important to ensure a complete and sustainable recovery. By addressing both aspects, neurorehabilitation offers patients a unique opportunity to regain their independence and improve their quality of life.
If you liked this blog post about the impact of neurorehabilitation on mental health, you will surely be interested in these NeuronUP articles:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
El impacto de la neurorrehabilitación en la salud mental: un enfoque integral para el bienestar cognitivo y emocional






 Fun Letter Game for the Little Ones: The Little Letter Glutton
Fun Letter Game for the Little Ones: The Little Letter Glutton
Leave a Reply