ADHD is the abbreviation for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. A disorder that affects between 2% and 5% of the child and adolescent population. At the school level it is estimated that in a class of 30 students between one and two students have ADHD.
This disorder is chronic and begins to reveal itself before the age of 7. It is also more frequent in boys than in girls. For every four boys with ADHD, one girl has it, according to data from the Spanish Federation of Associations for Assistance to Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.
It is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by overt symptoms of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity. There are three subtypes depending on which symptom predominates or if they are equivalent.
ADHD subtypes
- Predominantly inattentive: Children who have it have severe problems with inattention, but a lesser degree of hyperactivity or impulsive symptoms.
- Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive: Problems of hyperactivity/impulsivity predominate, but attention problems are not prominent.
- Combined: has severe problems with attention, hyperactivity and impulsivity.
How to recognize ADHD?
A timely diagnosis is the first step to prevent its complications. The main manifestations of each of the areas are:
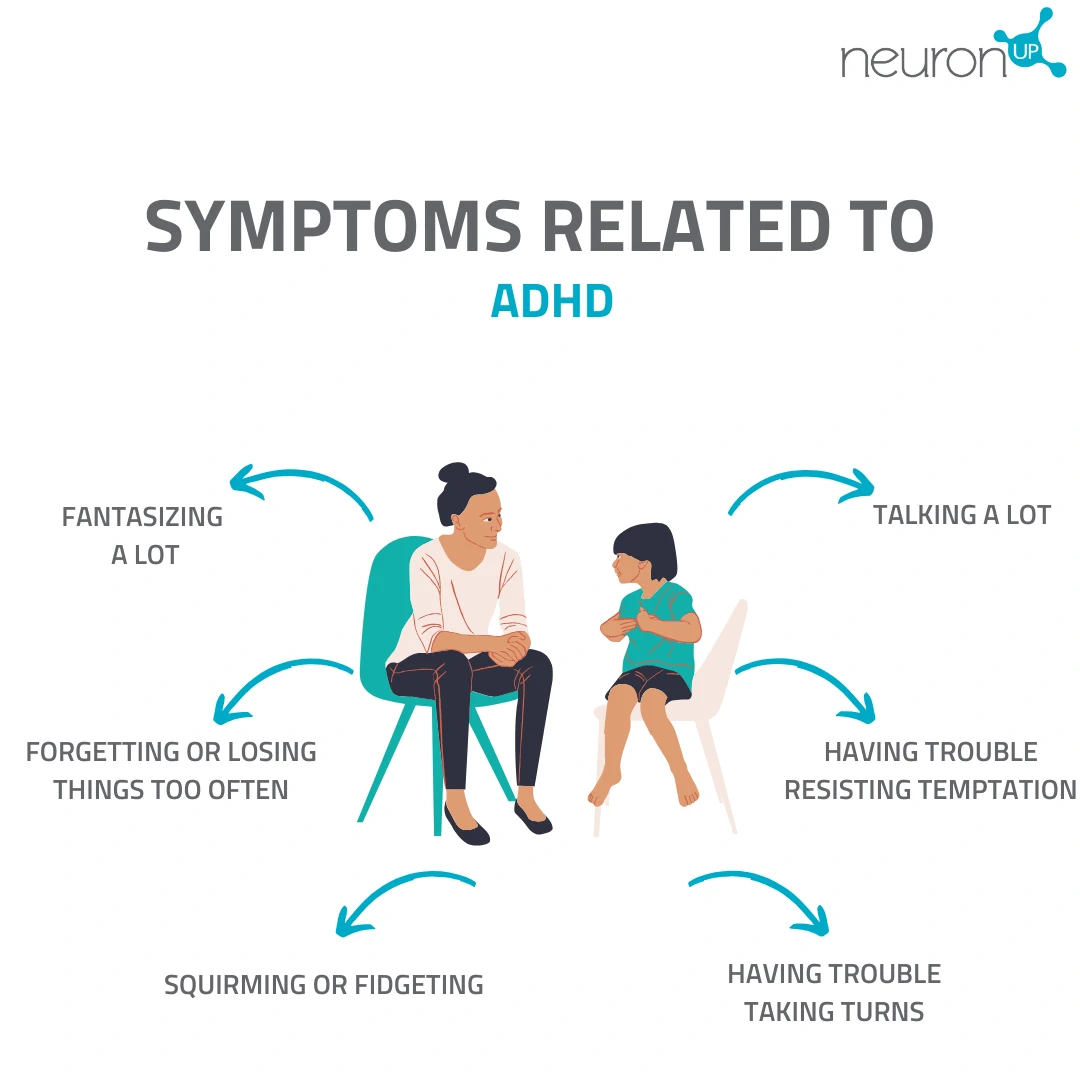
Inattention
- They have difficulty paying attention to details.
- They have trouble sustaining attention on tasks or activities.
- They make careless mistakes, for example, when doing homework.
- They are easily distracted by trivial stimuli.
- They seem not to listen when spoken to.
- They have difficulty following orders or instructions and completing tasks.
- They have difficulties organizing their activities or tasks.
Hyperactivity
- They fidget in their seat or excessively move their hands and feet.
- They get up in situations where they should remain seated.
- Excess energy.
- Runs or jumps excessively in inappropriate situations (in adults, a feeling of restlessness).
- Difficulty playing or engaging calmly in leisure activities.
- Talks excessively.
Impulsivity
- They rush to answer without allowing the question to be finished.
- They have difficulty waiting their turn.
- They interrupt or intrude on others’ activities.
How to address ADHD?
The treatment of children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder requires a multidisciplinary program, adapted to each child’s characteristics to improve their individual abilities and traits. It requires cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy, pharmacological treatment, and psychopedagogical intervention.
With the aim of addressing the cognitive deficits of children affected by ADHD, NeuronUP will offer next Tuesday cognitive rehabilitation activities for children with ADHD.
IMPACT OF ADHD ON THE SCHOOL AND SOCIAL LIFE OF CHILDREN
In the school environment, a child with ADHD faces additional challenges in meeting academic demands and adapting to classroom rules. We analyze how ADHD impacts academic performance, the ability to concentrate, interaction with classmates and teachers, and adaptation to the educational environment, and include strategies and recommendations based on recent studies to achieve better school inclusion and promote healthy social relationships.
ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE AFFECTED BY ADHD
Numerous studies have documented that ADHD has a significant negative impact on children’s academic performance. Compared with their peers without ADHD, these children receive lower scores on reading and math tests, lower academic averages, and are at greater risk of repeating a grade or being placed in special education classes. For example, it is common for a child with ADHD to know the material but not be able to complete an exam or assignment on time due to distractions, resulting in grades that do not reflect their true potential. In later stages, it has been observed that adolescents with ADHD lose more school years (repeat grades) and perform worse on standardized tests compared to their peers. These academic difficulties are often directly linked to the disorder’s symptoms: inattention interferes with learning and task completion, while impulsivity and hyperactivity can lead to disruptive behaviors in class.
A central factor is the difficulty in maintaining concentration. The inability to sustain attention is a core symptom of ADHD. Children with this disorder often get distracted easily, forget instructions or leave tasks incomplete as they lose focus quickly. Likewise, hyperactivity and impulsivity translate into problems staying seated and waiting turns, which disrupt both their own academic progress and that of their classmates. Consequently, the path to academic success presents more obstacles for a student with ADHD than for their average peers.
However, it is worth mentioning that with appropriate interventions (educational, behavioral and even medical) many children with ADHD can improve their academic performance. For example, multimodal treatment that combines pedagogical strategies with medical treatment has been shown to modestly increase grades and reduce the risk of school failure, which underscores the importance of detecting and addressing ADHD early.
SOCIAL INTERACTION WITH PEERS AND TEACHERS
ADHD not only affects grades; it also strongly impacts children’s social relationships with both peers and teachers. Among peers, children with ADHD often face difficulties fully integrating. Their impulsive behavior (such as interrupting conversations or games, or having emotional outbursts) and their constant distraction can be frustrating for other children. Studies indicate that the typical behaviors associated with ADHD often provoke social rejection. The reasons included patterns of impulsive and explosive behavior, which created an immediate negative impression in the group. It is common that these children, without intending to, interrupt their friends, do not follow the rules of a game or insist on imposing their idea in an activity, which can push others away.
The relationship with teachers is also usually affected. Hyperactivity and impulsivity can lead to more reprimands and constant corrections, generating tension in the classroom. A recent meta-analysis highlights that children with ADHD symptoms experience lower levels of emotional closeness and higher levels of conflict with their teachers, especially pronounced in younger children and those with hyperactive-impulsive presentations of the disorder. This can create a vicious cycle in the classroom: the child’s impulsive behaviors (interrupting, moving incessantly, not following instructions) increase the teacher’s frustration, who may respond with more frequent reprimands or negatives; in turn, these negative interactions increase the child’s dysregulation and behavioral problems.
Over time, these difficulties in social relationships can affect the child’s self-esteem and attitude toward school. A child who feels rejected by peers or in constant conflict with adults at school may come to associate school with frustration and stress rather than learning and friendship. In fact, specialists report that up to 80% of children with ADHD experience significant conflicts with their parents or teachers due to their behavior, which evidences the prevalence of the problem. This situation reinforces the need to intervene not only with the child but also in their social environment, to break the negative cycle and promote more positive interactions.
ADAPTATION TO THE EDUCATIONAL ENVIRONMENT
Due to the challenges described, the adaptation of a child with ADHD to the school environment usually requires additional supports. Schools typically demand that students follow a daily routine, attend to instructions, work independently and cooperate in groups; it is precisely in these aspects that ADHD can interfere. Many children with ADHD have difficulty adjusting to classroom rules and structure, which can lead to sanctions or frequent calls to attention.
Without appropriate strategies, the child may feel overwhelmed by the educational environment. Everyday transitions such as changing activities, moving from one classroom to another or simply going from recess to class can be especially difficult for them. It is common for these students to need constant reminders and close supervision to comply with their tasks and rules. Even those children with ADHD who do not qualify for special education often require additional help in the day-to-day school setting
Fortunately, schools can implement adaptations in the environment and classroom dynamics to facilitate the inclusion of students with ADHD.
The key lies in a multidimensional intervention: combining classroom adjustments (active methodologies, visual supports, positive reinforcements), training and awareness in the educational community (teachers and students informed about ADHD), parental involvement and, when required, medical or therapeutic treatment. Recent studies emphasize that addressing ADHD is not only the child’s matter but that of their entire environment – collaboration between family and school, as well as an empathetic school climate, can greatly mitigate the difficulties associated with the disorder.
If you liked this article about ADHD in children: symptoms, types and multidisciplinary treatment, you will likely be interested in these NeuronUP articles:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
ADHD en niños: síntomas, tipos y tratamiento multidisciplinar



 Mirror Neuron System: function, dysfunction, and rehabilitation proposals
Mirror Neuron System: function, dysfunction, and rehabilitation proposals
Leave a Reply