Occupational therapist, Olalla Sáiz Vázquez, explains how to carry out an intervention with NeuronUP in older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The group to be worked with is a group of five users with MCI from the Mevefares Residential Center.
Mild cognitive impairment is considered when cognitive decline exceeds what is expected for the user’s age but does not meet the criteria to be called dementia. For it to be considered MCI there must be problems with memory, preserved functionality, and no diagnosis of dementia.
There are four subtypes of MCI: amnestic, multidomain amnestic, non-amnestic and non-amnestic multidomain; therefore users may present a memory dysfunction or dysfunction of other higher functions, such as language or attention.
In the assessments carried out at the center, using the MMSE and the Clock Drawing Test, it can be seen that users present mild difficulties in Time Orientation, in language, in sustained attention and, above all, in memory; therefore it is decided to intervene on these aspects.
Objectives of the intervention in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
The main objective is to improve the affected cognitive skills to prevent possible progression to dementia in older adults who present mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
In addition, a series of specific objectives are proposed:
- Improve sustained attention.
- Maintain Time Orientation.
- Develop working memory.
- Improve logical reasoning.
- Strengthen semantic memory as well as vocabulary.
- Develop problem-solving ability.
Cognitive session for older adults with MCI
To carry out the intervention in people with MCI the users will perform the following exercises, with an estimated time of 45 minutes.

1. Location in Time
What does it consist of?
This activity consists of choosing the correct answer from several options. It is made up of questions related to Time Orientation, such as the day, the time, the season of the year or the month; among others.
Duration: 5 minutes.
What does this activity train?
The aim of this activity is to improve Time Orientation.
Languages
This worksheet is available in Spanish, English, French, Portuguese, Catalan, German and Italian.
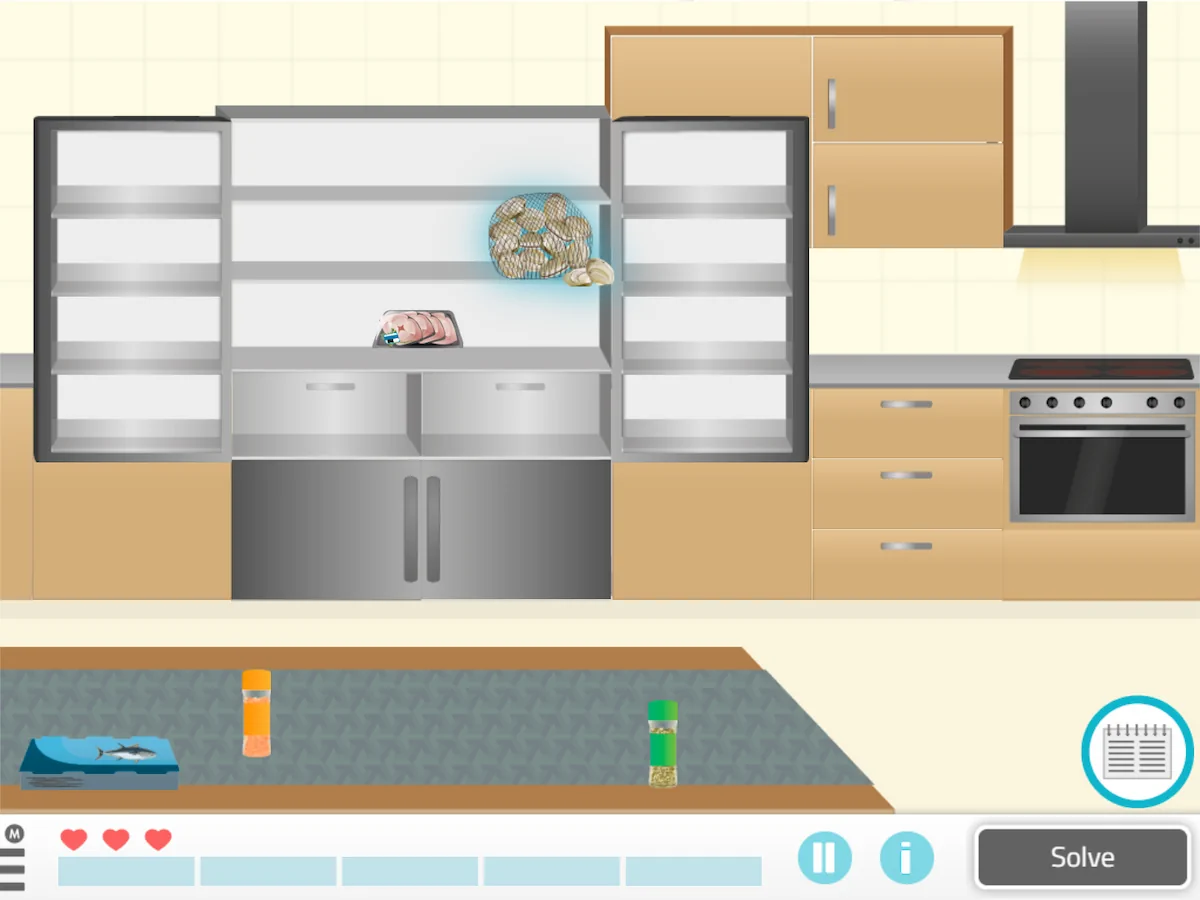
2. Straighten Up the Kitchen
In this exercise an image of a kitchen and different items that must be stored on the shelves, in the fridge or in the freezer will appear on the screen. By hovering the cursor over the different storage places, they will be able to see what is stored there. Likewise, it is important to remember what is stored in each place to take the minimum possible time.
Duration: in this case, 10 minutes are set to complete the activity.
Difficulty level: stages 1 and 2.
What does this activity train?
This activity aims to
- Strengthen semantic memory and also short-term memory.
- Develop reasoning ability.
- Improve sustained attention.
Languages
This game is available in Spanish, English, French, Portuguese, Catalan, German and Italian.
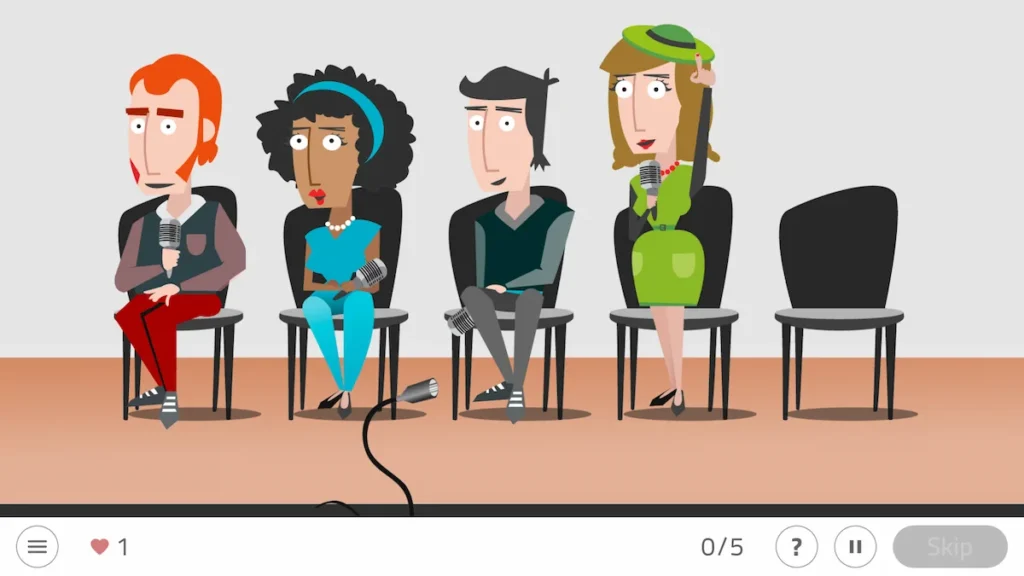
3. Press Conference
In this activity the user will see people sitting in a waiting room. They will get up one by one, following an order that the user will have to replicate. Therefore, they will have to click on the people who have stood up following the same order.
Duration: 5 minutes.
Difficulty level: stages 2 and 3.
What does this activity train?
This activity aims to:
- Improve working memory.
- Develop sustained attention.
Languages
This game is available in Spanish, English, French, Portuguese, Catalan, German and Italian.

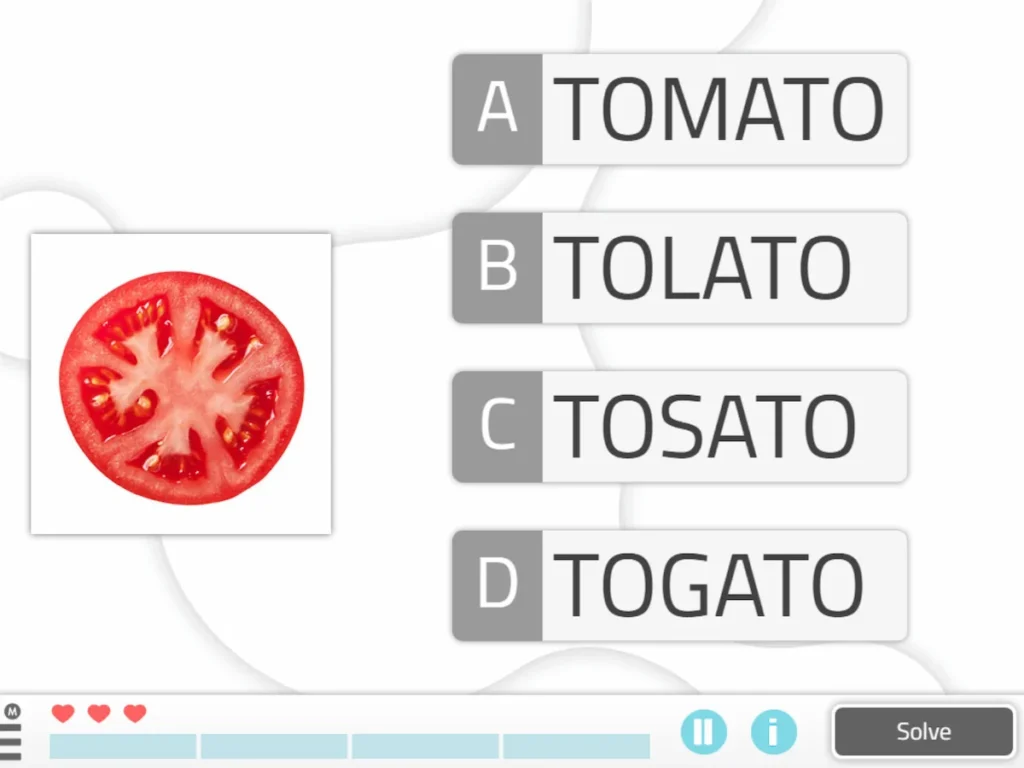
4. Correct Image Name
An image and five answer options will appear on the screen, among which is the name of the item shown in the image. Therefore, the user will have to identify the correct one among those that contain spelling mistakes or other words and click it.
Duration: 10 minutes.
Difficulty level: hard.
What does this activity train?
This activity aims to:
- Develop semantic discrimination.
- Strengthen semantic memory and also short-term memory.
- Improve sustained attention.
Languages
This worksheet is available in Spanish, English and Portuguese.
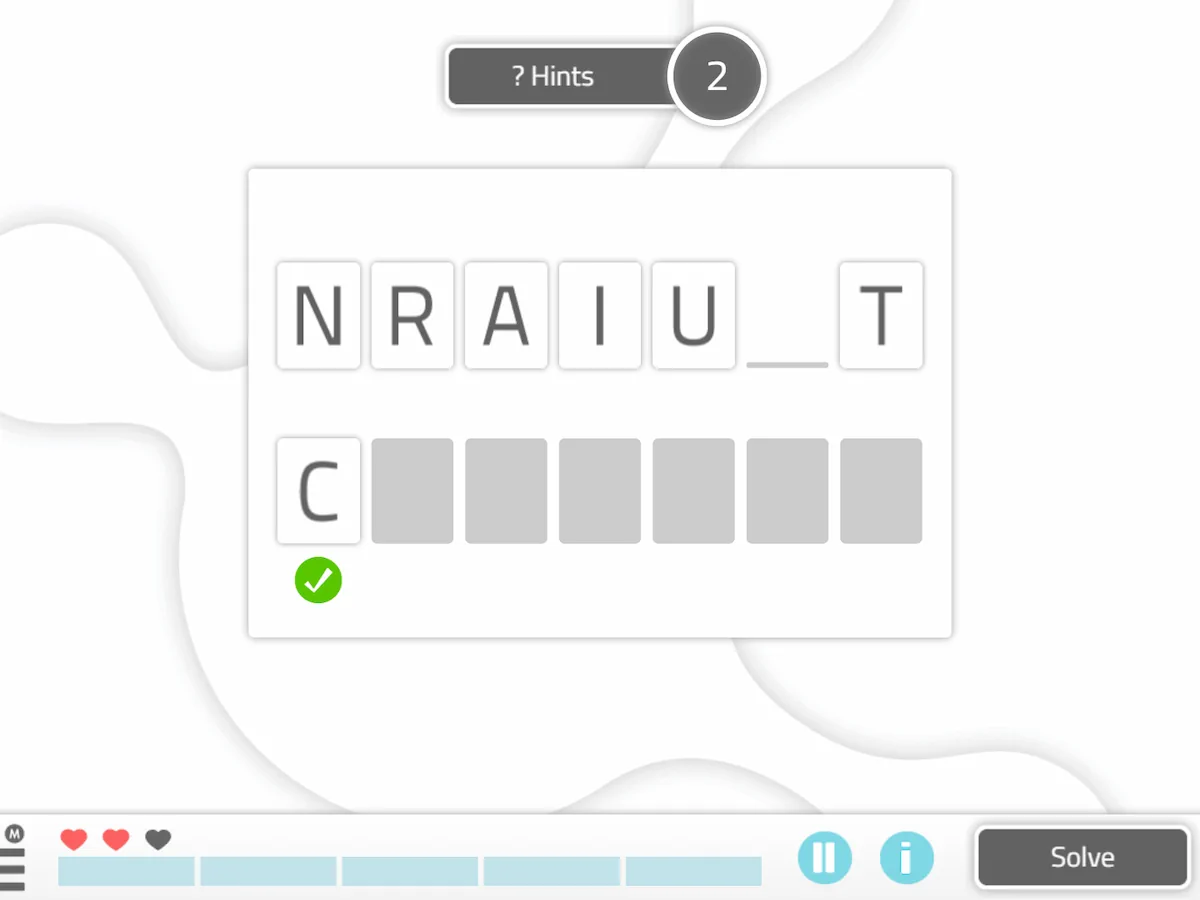
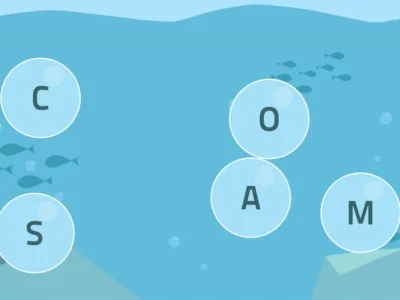
5. Word Scramble
In this activity the user will have to arrange the letters that appear on the screen to form a word.
Duration: 10 minutes.
Difficulty level: stages 2 and 3.
What does this activity train?
This activity aims to:
- Improve semantic memory.
- Increase vocabulary.
- Develop sustained attention.
Languages
This game or generator is available in Spanish, English, French, Portuguese, Catalan, German and Italian.
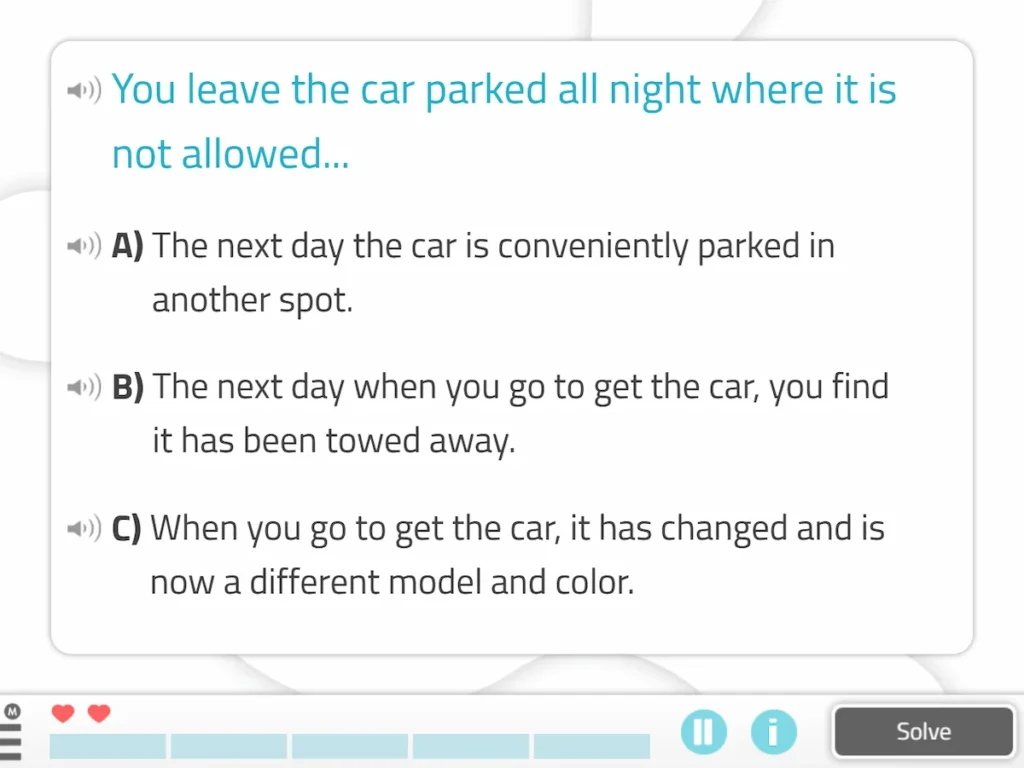
6. Consequences
A situation will appear on the screen and the user will have to choose which of three options is the consequence that action would have.
Duration: 5 minutes.
Difficulty level: medium.
What does this activity train?
This activity aims to develop logical reasoning.
Languages
This worksheet or generator is available in Spanish, English, French, Portuguese, Catalan and German.
Conclusions on the intervention with NeuronUP in older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
There is a belief that older people have greater difficulty using ICTs. However, with an intuitive and easy-to-use platform like NeuronUP they can perform different tasks on the computer or tablet satisfactorily.
In addition, performing them on the computer also works on fine motor skills when moving the mouse, and on sustained attention because it is a medium they are less familiar with than paper.
Finally, to achieve the greatest success in interventions for people with MCI, it is advisable to combine this type of session with other cognitive activities, such as work therapy or paper worksheets.
Bibliography
- Custodio N, Herrera E, Lira D, Montesinos R, Linares J, Bendezú L. Deterioro cognitivo leve: ¿Dónde termina el envejecimiento normal y empieza la demencia? An. Fac. med. 2012; 73 (4)
- Meléndez Moral JC, Sanz-Álvarez T, Navarro-Pardo E. Deterioro cognitivo leve: método y procedimiento de clasificación. An Psicol [Internet]. 1 de mayo de 2012 [citado 1 de diciembre de 2020]; 28(2):604-10. Disponible en: https://revistas.um.es/analesps/article/view/analesps.28.2.148891
In addition to Olalla Sáiz, Menduiña Besada and Alba Sáiz Vázquez contributed to the making of this article.
If you liked these activities aimed at older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), you may be interested in these NeuronUP articles:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
Intervención con NeuronUP en mayores con deterioro cognitivo leve (DCL)




 Dyslexia as a barrier in childhood
Dyslexia as a barrier in childhood
Leave a Reply