Today we launch the updated game Plans in Action to improve attentional skills in children.
What does this activity involve?
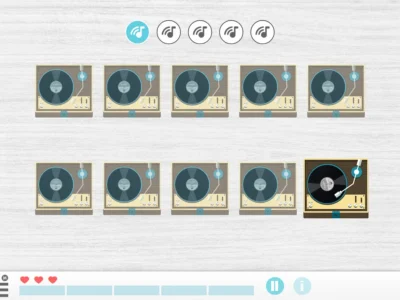
Below, we show you an example of the Plans in Action activity:

What does this activity train?
By doing this game, we are training attentional skills, specifically selective attention and sustained attention, in addition to inhibitory control and working memory.
This activity aims to reproduce the layout, so that what is on the right side is recreated on the left side with as few clicks as possible.
To be able to replicate the sequence, we will have to click on the squares on the left side until the correct piece appears.
During the activity, the user must attend to relevant stimuli and ignore irrelevant ones to complete it.
Play through levels
This children’s game is divided into twelve stages, with the first stage being the easiest and the twelfth the most difficult.
The user will move up or down a level automatically based on their correct responses or mistakes. Additionally, the professional can choose the stage manually.
Activity customization
This activity can be played in the default timed mode or default untimed:
Default timed:
- The user will have a maximum time to complete the activity,
- there will be no visible timer,
- they must pass 1 exercise to advance a stage,
- they must fail 1 exercise to move down a stage.
Default untimed:
- The user will not have a maximum time to complete the activity,
- there will be no visible timer,
- they must pass 1 exercise to advance a stage,
- they must fail 1 exercise to move down a stage.
Application to daily life
Children should be able to copy models, organize visual information and spatial Follow Instructions. For example, at the Right Now of performing school tasks such as copying information from the board, completing patterns or Follow Instructions.
It can be applied when doing puzzles, for example, building a LEGO, Finish the Drawings or following a map.
Recommended for:
For children with difficulties in attentional regulation and/or inhibitory capacity mainly; as may appear in some neurodevelopmental disorders, such as ADHD and autism; in learning difficulties, such as dyslexia, dyscalculia or dysgraphia; in intellectual disability; and Down syndrome.
If you liked this attentional skills game for children, you may also be interested in these articles:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
Juego de habilidades atencionales: Planos en acción





 The Role of the Caregiver in Brain Injury Rehabilitation (BI)
The Role of the Caregiver in Brain Injury Rehabilitation (BI)
Leave a Reply