Do you know what activities of daily living are? Do you know the difference between basic and instrumental activities? Do you know how to work on them?
What are activities of daily living (ADLs)?
Activities of daily living (ADLs) include all those everyday activities that have a specific value and meaning for a person and, furthermore, a purpose. However, occupations are central to a person’s identity and abilities and influence the way one uses time and makes decisions.
Classification of ADLs
We can classify activities of daily living into several groups.
Basic activities of daily living (BADLs)
Basic activities of daily living are activities oriented toward self-care such as: bathing or showering, dressing, eating or sleeping. These activities also include care of the bladder and bowels, functional mobility and care of personal assistive devices. As well as sexual activity, personal hygiene and grooming, and toilet hygiene.
Instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs)
Instrumental activities of daily living are activities oriented toward interaction with the environment. They are often complex and, generally, optional, since they can be delegated to others. Some instrumental activities of daily living are:
- Care of others (including selection and supervision of caregivers),
- pet care,
- raising children,
- use of communication systems,
- community mobility,
- management of financial matters,
- health care and maintenance,
- creating and maintaining a home,
- meal preparation and cleaning,
- safety procedures and emergency responses,
- going shopping.
Advanced activities of daily living (AADLs)
Education
These are the activities necessary to be a student and participate in the educational environment through actions such as:
- Participation in formal education,
- exploration of personal education needs or interests,
- personal participation in informal education.
Work
In this classification, we find the activities necessary to obtain employment, whether paid or volunteer activities. The characteristics of these activities are:
- Interest in and search for employment,
- finding and securing a job,
- job performance,
- preparation for retirement,
- exploring volunteering,
- voluntary participation.
Play
These are spontaneous or organized activities that provide enjoyment, entertainment, pastime or fun. For example: participatory games and exploration of other games.
Leisure
In general terms, these are non-obligatory activities chosen voluntarily. They are also characterized by being performed during a time that does not conflict with dedication to obligatory occupations such as work, personal care or sleep. This type of activity is aimed at: exploration of free time and preparation for leisure.
Social participation
These are activities associated with the organization of behavior patterns that are characteristic and expected in an individual or collective interaction with others within a given social system. This type of activity is carried out in relation to:
- Community,
- family,
- partner / friend.

Subscribe
to our
Newsletter
10 exercises to work on ADLs
Below, we will list several exercises to work on basic and instrumental activities offered by NeuronUP for both children and adults. First, we start with exercises to work with adults.
Exercises to work on activities of daily living with adults
1. Get Dressed
First, we propose this exercise which would be an ideal example for working with patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
What does it involve?
It consists of dressing the silhouette appropriately, taking into account both the placement and order of each garment as well as the type of situation.

What does this activity work on?
With this exercise we work on procedural memory, body schema, ideational praxias, semantic memory and planning.
Play by levels
There are six levels. In the simplest levels there are fewer instructions and more program prompts to perform the activity correctly, while in the most difficult levels the prompts decrease and the clothing requirements are more complex.
Personalization of the activity
In addition, you can personalize the activity to suit each user’s abilities.
Parameters
You can select the number of garments, the scenario, whether to include any type of distractor, the errors that can be made, the presentation of the garments, etc.
General aspects
You can choose the number of exercises, the maximum time, whether or not you want a visible timer for the activity and modify the execution instructions, etc.
Adaptability
Finally, you can select whether you want the clothing items to be draggable or only by tapping/clicking on the garment it is selected. Depending on the user’s functionality you can choose one option or the other.
2. Recycle the garbage
What does it involve?
This daily living exercise consists of placing the different types of waste in their corresponding bin or container:
- Yellow: packaging (plastics and cans),
- Blue: paper and cardboard,
- Green: glass,
- dark green/ red container: organic waste.
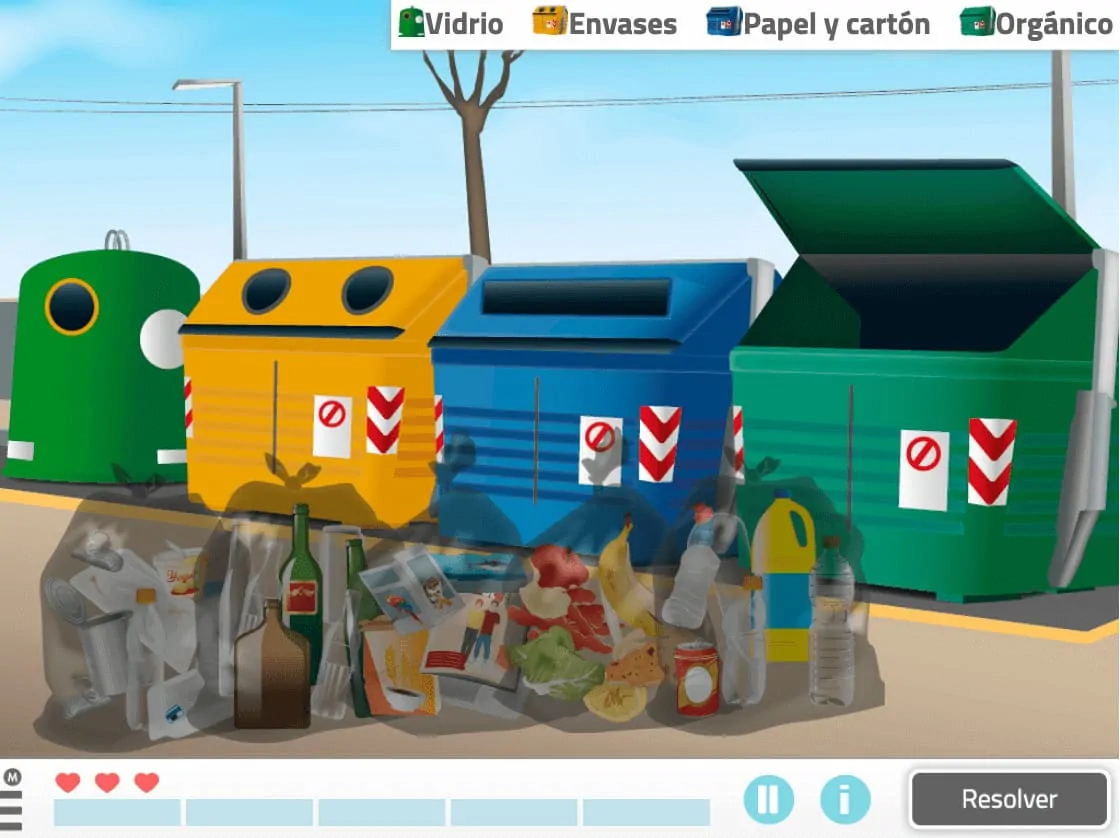
What does this activity work on?
This activity primarily exercises memory and reasoning.
3. Accurate Payments
What does it involve?
Through this exercise, the therapist encourages the user to select the exact amount of money requested .
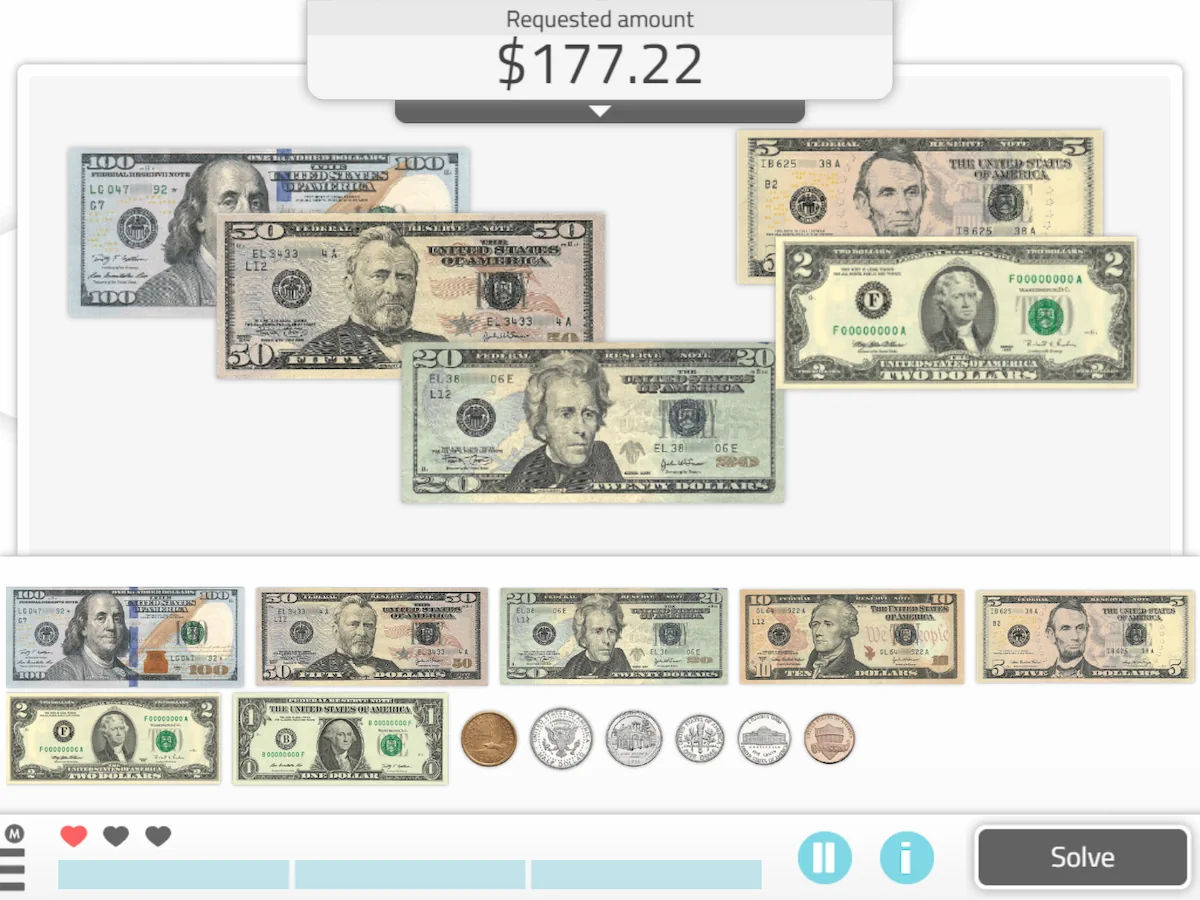
Personalization of the activity
We can personalize the activity and select the currency we want to work with: euros, dollars, pesos, etc.
We can also select the range of amounts, whether we want decimals, etc.
What does this activity work on?
It is an exercise highly focused on people with Alzheimer’s. We will be working on working memory, shopping and planning.
4. Objects, places and professionals
What does it involve?
In this exercise the user has to match various objects with the places where they are obtained and the professionals who are responsible for them. In addition, we can work on a multitude of alternatives, starting with something simple like varying the objects and places each time.
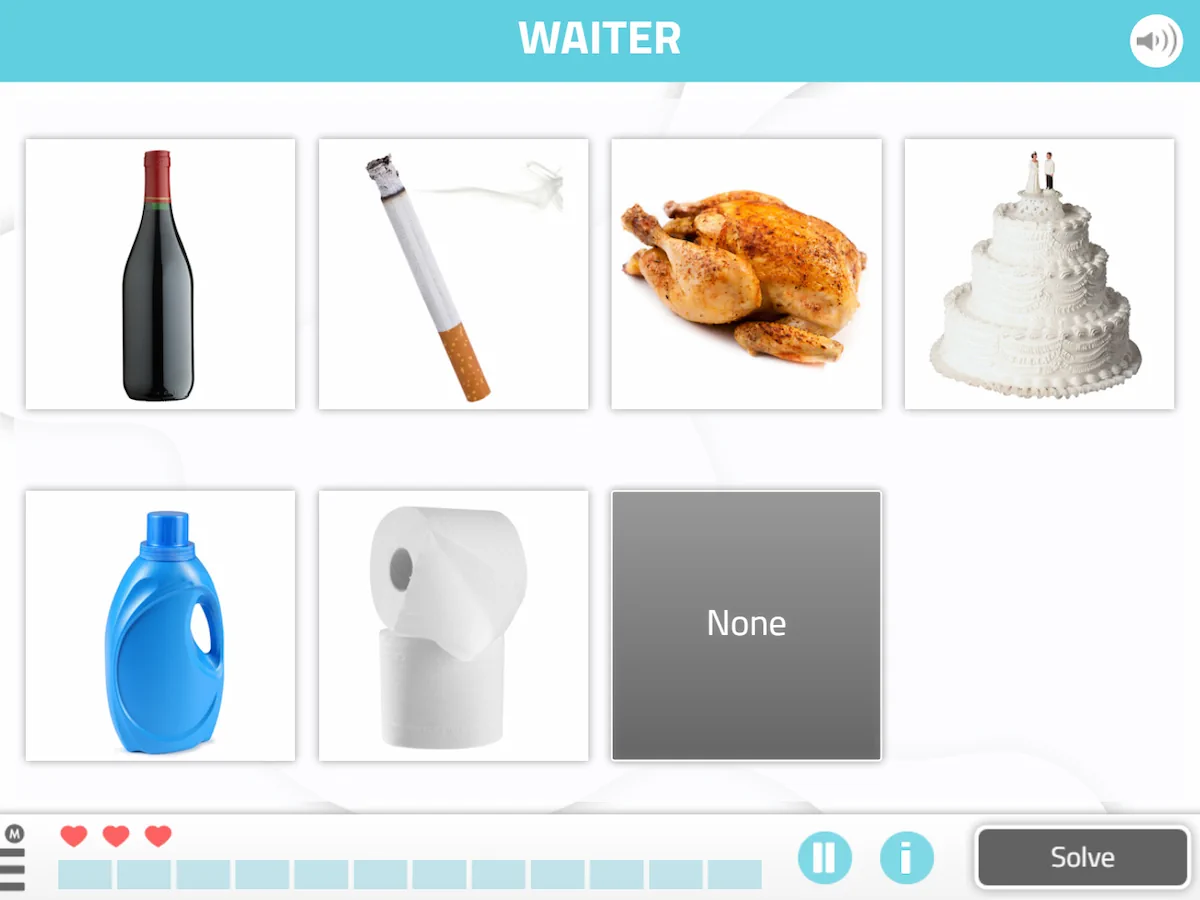
What does this activity work on?
In this instrumental activities of daily living worksheet, Place Orientation and shopping are worked on.
5. Pick Up your Baggage
What does it involve?
In this game you must select only the suitcases identical to the model among a set of moving luggage. Depending on the phase, more suitcases will appear to recognize.
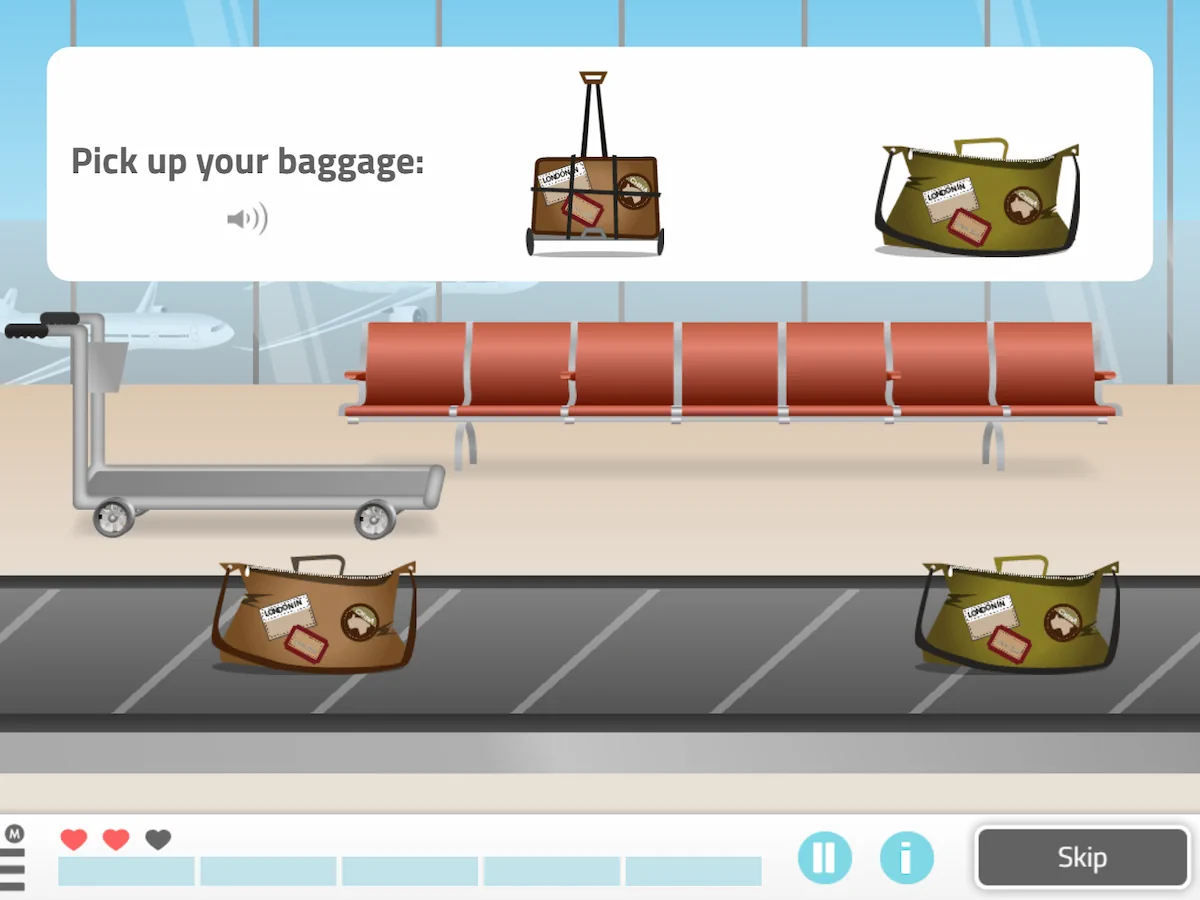
What does this activity work on?
In this exercise for adults, selective attention, sustained attention, working memory, processing speed and leisure are worked on.
6. What’s Making Noise in the Kitchen?
What does it involve?
This exercise consists of identifying the sounds heard in the context of a kitchen. The user must listen carefully to the noises and tap/click on the object that makes each sound.

What does this activity work on?
This game works on auditory gnosias, the kitchen and cleaning.
7. Straighten Up the Kitchen
What does it involve?
In this exercise users must place the kitchen objects in their corresponding places.
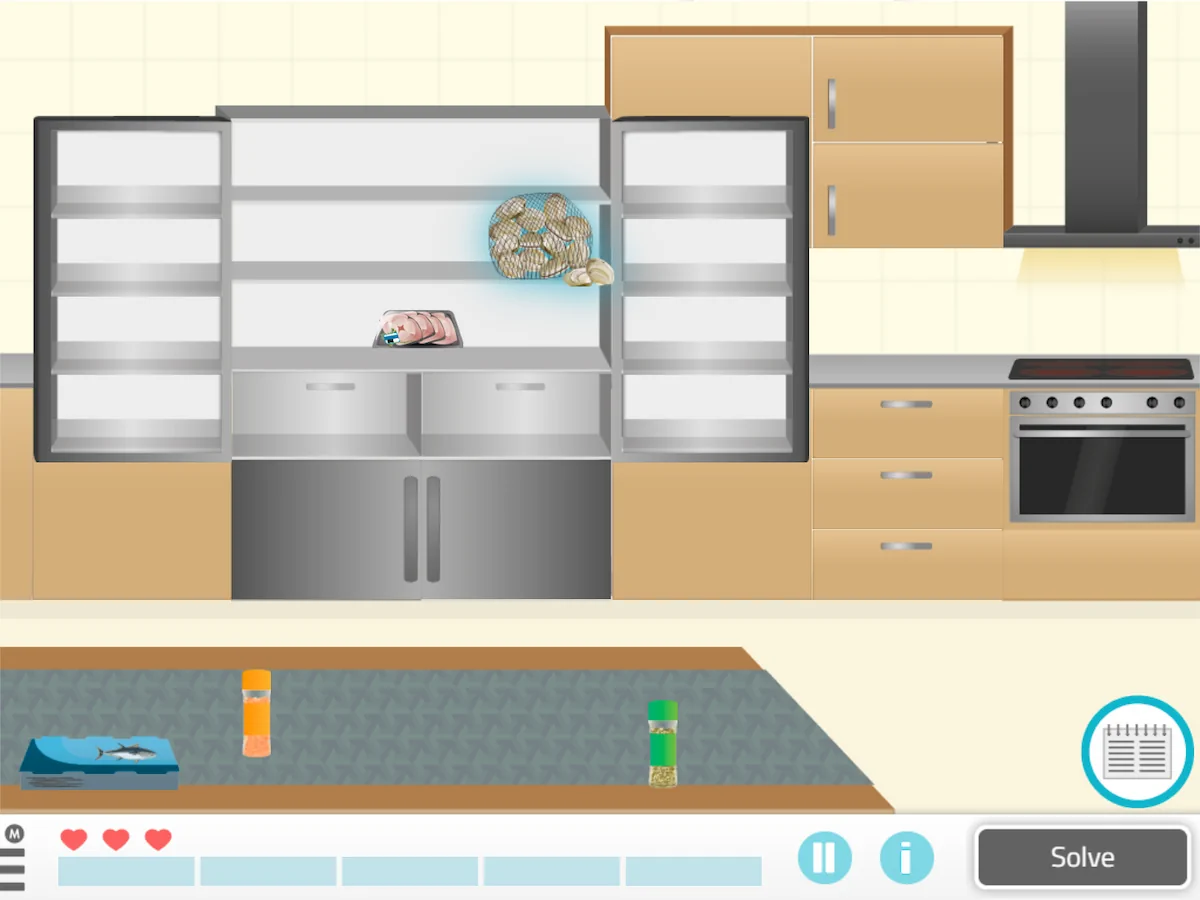
What does this activity work on?
Consequently, sustained attention, semantic memory, episodic memory and reasoning are worked on.
Exercises to work on activities of daily living with children
Below, we present several exercises to work with children and adolescents:
8. Pack your Backpack
What does it involve?
It is a game in which children have to prepare the backpack for school, selecting only the objects necessary for that day.
The objective of this daily living activity is for children not to forget anything. In addition, it also aims to prevent them from putting materials they do not need into their backpack and making it heavy. The challenge is on!
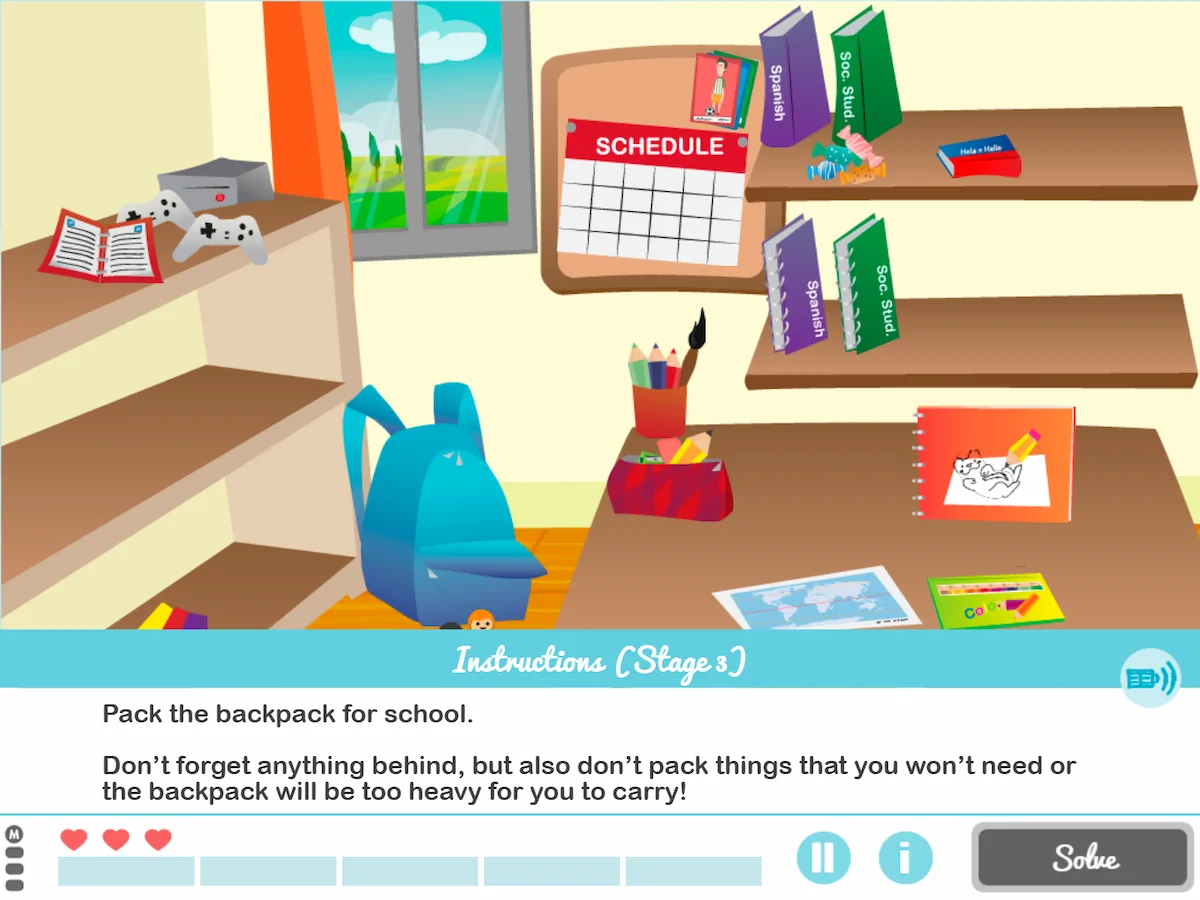
What does this activity work on?
It is a children’s activity to work on planning, that is, the child works on what to take based on the subjects they have each day. It also stimulates selective attention.
9. Step by Step (Picture-Only)
What does it involve?
This worksheet to work on planning and reasoning consists of putting in order the different steps necessary to perform an activity.

10. Step by Step (Text-Only)
The last of the activities of daily living we propose today is Step by Step.
What does it involve?
It is the same as the previous activity, but in this case the steps to carry out an activity are worked on with written content instead of drawings.
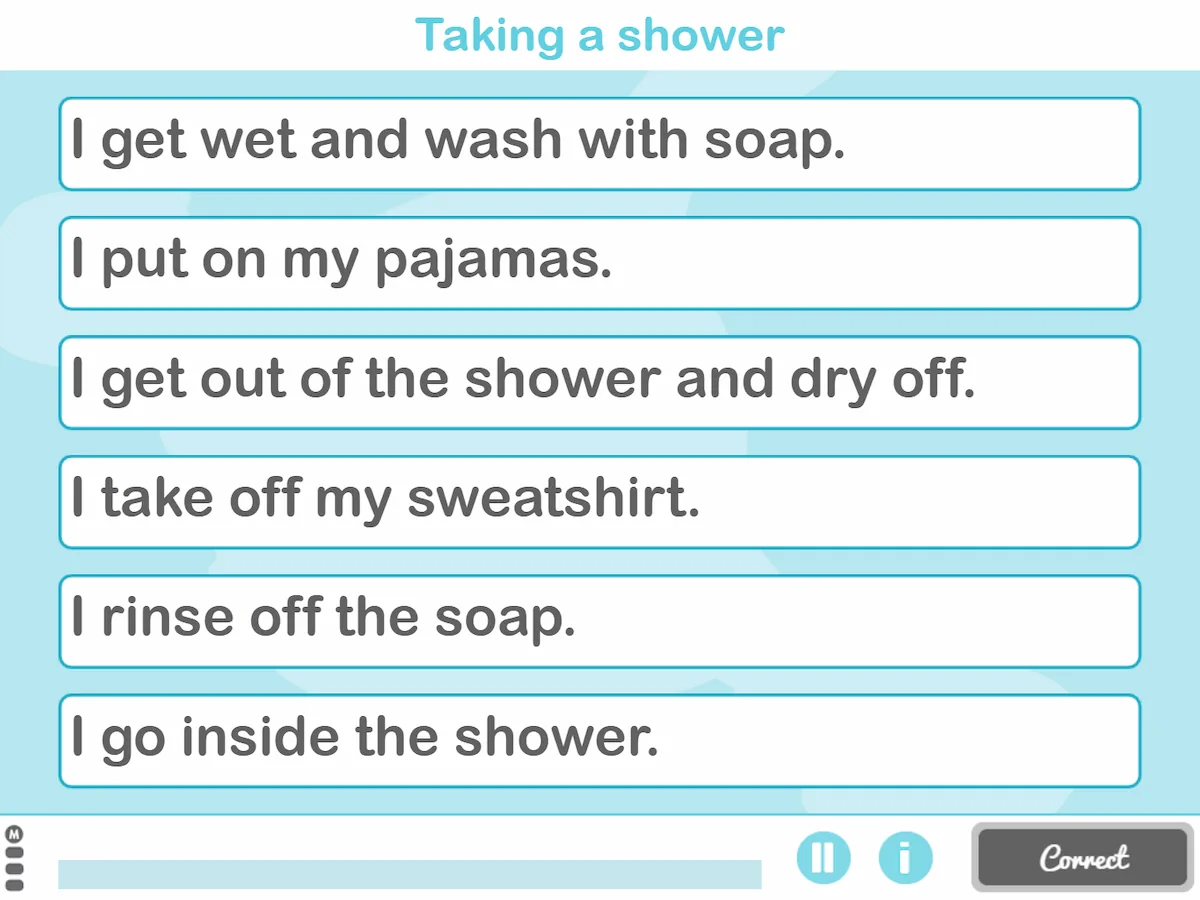
What does this activity work on?
In addition to helping stimulate planning and reasoning. Likewise, comprehension is worked on.
Conclusion
Activities of daily living (ADLs) are all those activities that both children and adults use in their day-to-day life. These activities have a specific value and meaning for a person and, furthermore, an individual purpose. ADL exercises allow people with neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s to work on attention and memory. Other functions such as reasoning, planning and comprehension are also worked on.
If you want to work with your patients on the above NeuronUP exercises to work on activities of daily living, request your free NeuronUP trial:
If you liked this post about activities of daily living, you might be interested in these NeuronUP posts:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
Actividades de la vida diaria (AVDs): definición, clasificación y ejercicios





 The Neurosciences and Their Evolution Over Time
The Neurosciences and Their Evolution Over Time
Leave a Reply