This article explains how ecological validity is addressed in NeuronUP and provides examples of some ecologically valid exercises from our platform.
What is ecological validity in neuropsychology?
Ecological validity in neuropsychology refers to the correspondence between the improvement of the skills trained in clinic and their relationship with better performance in day-to-day activities.
Ecological values in rehabilitation
We do not intend to make an exhaustive review of the concept of ecological validity, but to highlight a couple of important concepts. Some people may think it is sad to have brain impairment or to get older and be put in front of a computer screen. It can become frustrating and can even have a motivational impact, a fundamental aspect in functional recovery. At NeuronUP we think exactly the same.
We do not believe in computerized rehabilitation when it can do more harm than good. We do not believe in video games if they do not produce a positive effect.
We always say that the goals of a rehabilitation program must be tailored to our patient’s cognitive profile, but also to their preferences and motivations. The same applies to format. We cannot expect a computer to be motivating when it has never been, although we can run a prior motivational program so they become familiar with this format.
It is ironic that the concept “ecological” applied to validity comes from the experimental world. Brunswick (1956) was the first to use that term to establish the degree of relationship between a proximal cue and a distal variable in perceptual experiments. The capacity for generalization was opposed to the representativeness of the task. Today those concepts have changed.
Functionality
We say that goals must be adjusted to the cognitive profile. True. But the main objective is functionality, not numerical recovery in constructs.
Functionality and constructs are two common concepts in neuropsychological rehabilitation. According to Burgess et al. (2006) a third concept could be included, that of operations, giving us the triad of levels of analysis in neuropsychology.
Therefore, there are:
- Constructs: theoretical, inferred, such as working memory;
- operations: established from correlations between variables manipulated in a task and BOLD activity level –oxygen consumed by the brain–;
- functions: directly observable, they are the result of the interaction between a cognitive system and a goal that can be internal or externally elicited, such as social behavior.
What do these three concepts have to do with the idea of ecological validity?
Each of them is a level of analysis from which we start to build activities. And each of those activities has a different scope.
Kvavilashvili and Ellis (2004) detail three ecological levels in activities.
- Level one corresponds to the generalization that exists between two identical tasks.
- Level two corresponds to the generalization that occurs between a rehabilitation task and tasks that require similar processes.
- Level three refers to the generalization of what is learned to untrained activities and functions.
This means two things:
- That rehabilitation activities must be representative and predictive. Representative means that the task we are using in rehabilitation is related to (or operationally overlaps with) a real-life task.
- And predictive capacity means that performance on that “laboratory” task generalizes to other everyday tasks.
Ecological validity in assessment
When we assess, we use abstractions (tests), representations of the external world that are simplified. We think (intuitively?) that an “ecological” task in assessment compromises the psychometric values needed. But several studies (for example, with the Zoo test or the Multiple Errand Test) show more satisfactory values than the most consolidated assessment tests.
Let’s ask two questions:
- Why do many executive function tests fail to detect executive symptoms? Possibly because they are multifactorial (like the WSCT), because their design had to do with purposes different from the original (as happens with the Stroop Test), or because they are more complex than we think (like the Towers of London). But above all, because the reality of a theory that composes a task goes beyond the data.
- Should we do the same in rehabilitation? Should we operate at a theoretical, constructs level to devise neuropsychological rehabilitation activities? If what we want are ecological tasks, no. We are aware that it is not necessary for all rehabilitation tasks to be ecological because many serve to make people improve in concrete operations. But if the final objective is functionality, we must do likewise to design tasks that have contact with real activity.
Ecological validity: the patient at the center
We cannot force people in rehabilitation to adapt to the format we give them. That is why computerized rehabilitation may not be relevant. When we talk about ecological, the patient is included in the concept. Paraphrasing a well-known credit card brand: “For everything else, NeuronUP”.
Exercises with ecological validity
Below, we mention some ecologically valid exercises from NeuronUP:
1. Task Sequencing
What does it consist of?
In this activity the user has to put in order the different steps necessary to carry out an activity.
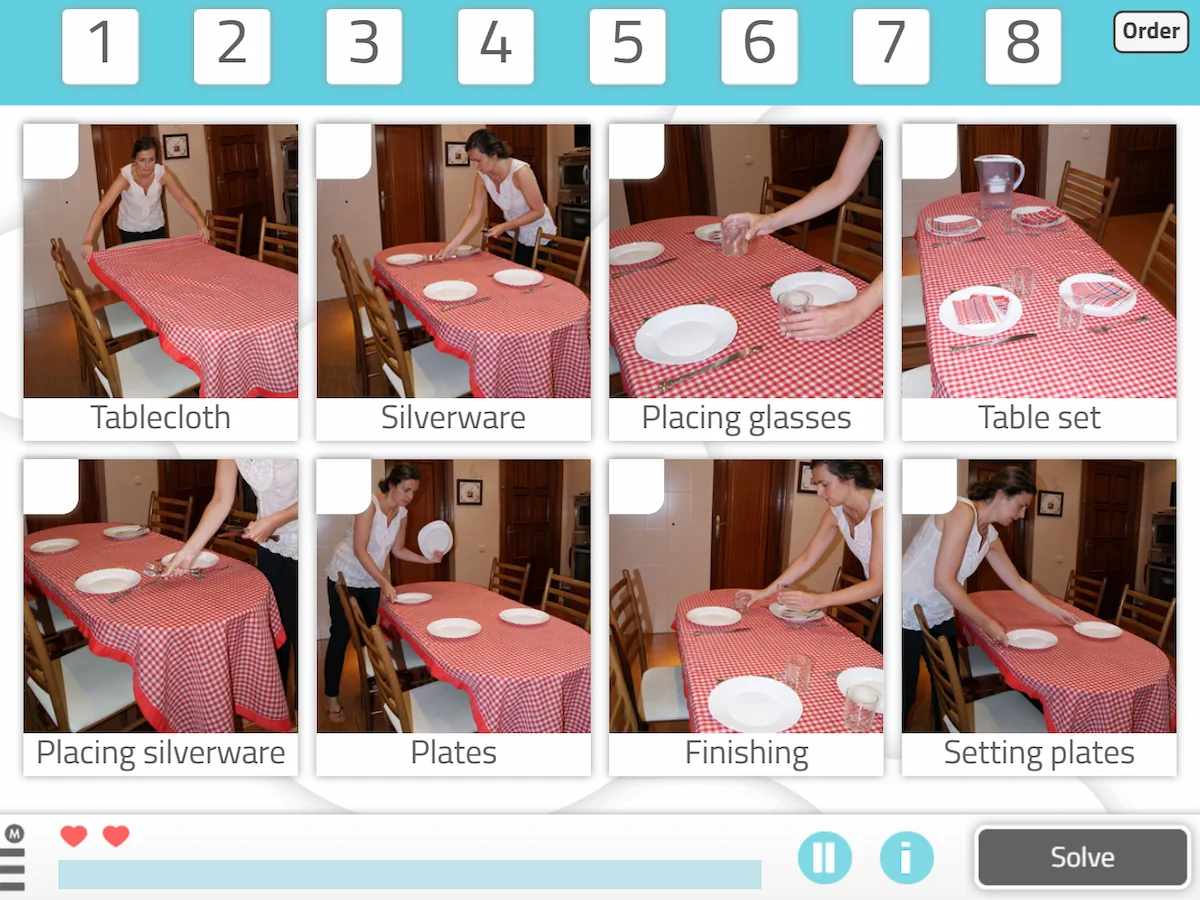
In the image, for example, the idea would be to number, according to the order in which they naturally occur, all the steps necessary to shop.
What does this activity work on?
As a primary function it works on planning and as a secondary one, reasoning.
Play by levels
It is organized into five difficulty levels: basic, easy, medium, hard and advanced.
Child version
This activity also has a child version called Step by Step.
Format
It is also available in text format. And it can be done both in digital and on paper.
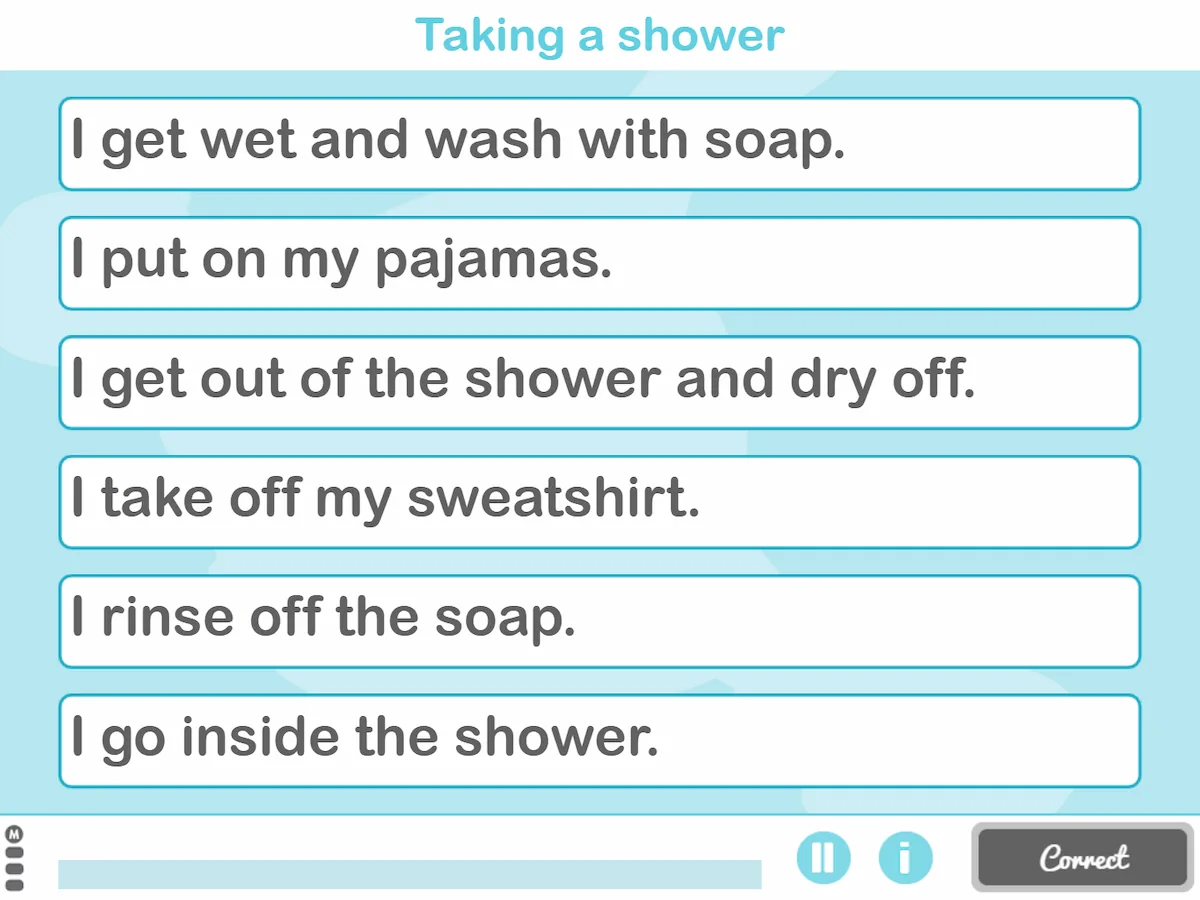
2. What’s Making Noise in the Kitchen?
What does it consist of?
This exercise with ecological validity consists of identifying the sounds heard in the context of a kitchen. First, the user must listen carefully to the noises, then they must click on the object that makes each sound. In the video below we show you an example:

What does this exercise work on?
On the one hand, this game works on the auditory gnosias. It also works on cooking and cleaning.
Play by levels
This game has 9 phases of difficulty.
Activity customization
You can customize this activity to adapt it to the individual needs and abilities of each person, being able to configure the general aspects and the parameters:
Parameters
On the one hand, the parameters, where you can select:
- Recognition difficulty,
- number of elements,
- number of audios,
- response time,
- maximum errors.
General aspects
And, on the other hand, you can adjust general aspects such as the number of exercises, the maximum time, whether or not you want the visible stopwatch for the activity and an inactivity warning or you can modify the instructions if you wish.
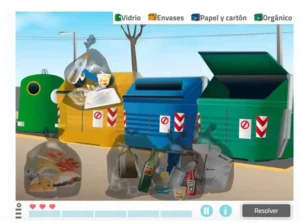
3. Recycle your trash
What does it consist of?
The user has to place different types of trash in their corresponding bin.
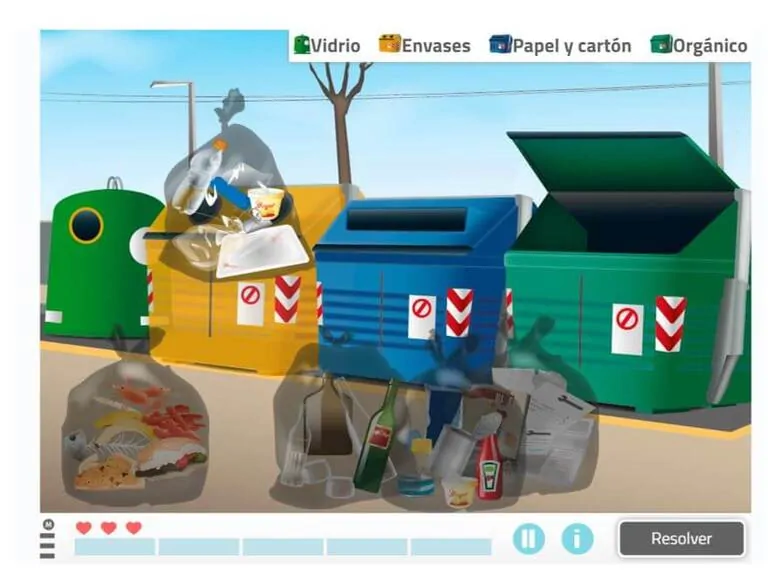
What does this activity work on?
This activity works on:
- Reasoning,
- sustained attention,
- semantic memory,
- episodic memory,
- cooking and cleaning.
Play by levels
This game has 9 phases of difficulty.
Activity customization
You can customize this activity to adapt it to the individual needs and abilities of each person, being able to configure the general aspects and the parameters:
Parameters
On the one hand, the parameters, where you can select:
- Scenario,
- number of elements,
- maximum errors,
- helps: object poster, bin poster, list and placed object.
General aspects
And, on the other hand, you can adjust general aspects such as the number of exercises, the maximum time, whether or not you want the visible stopwatch for the activity and an inactivity warning or you can modify the instructions if you wish.
4. Correct Image Name
What does it consist of?
It consists of discriminating the word that corresponds to the presented image.
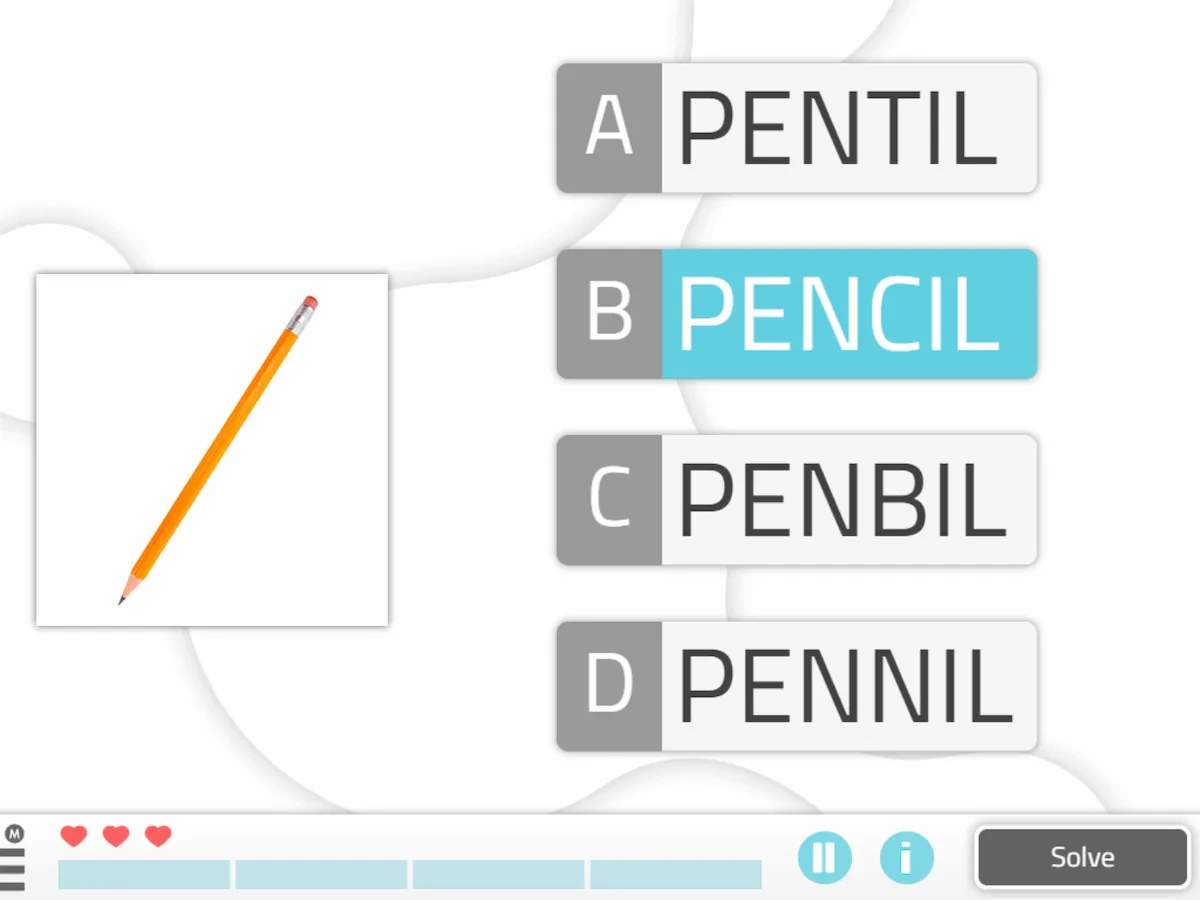
Play by levels
On the other hand, the activity What is the best thing to do? is organized into five difficulty levels: basic, easy, medium, hard and advanced.
Format
This worksheet is available both in digital and in paper format.
5. Get Dressed
What does it consist of?
This activity consists of dressing the silhouette appropriately, taking into account both the place and order of placement of each garment and the type of situation.
There is a male silhouette version and a female silhouette version.
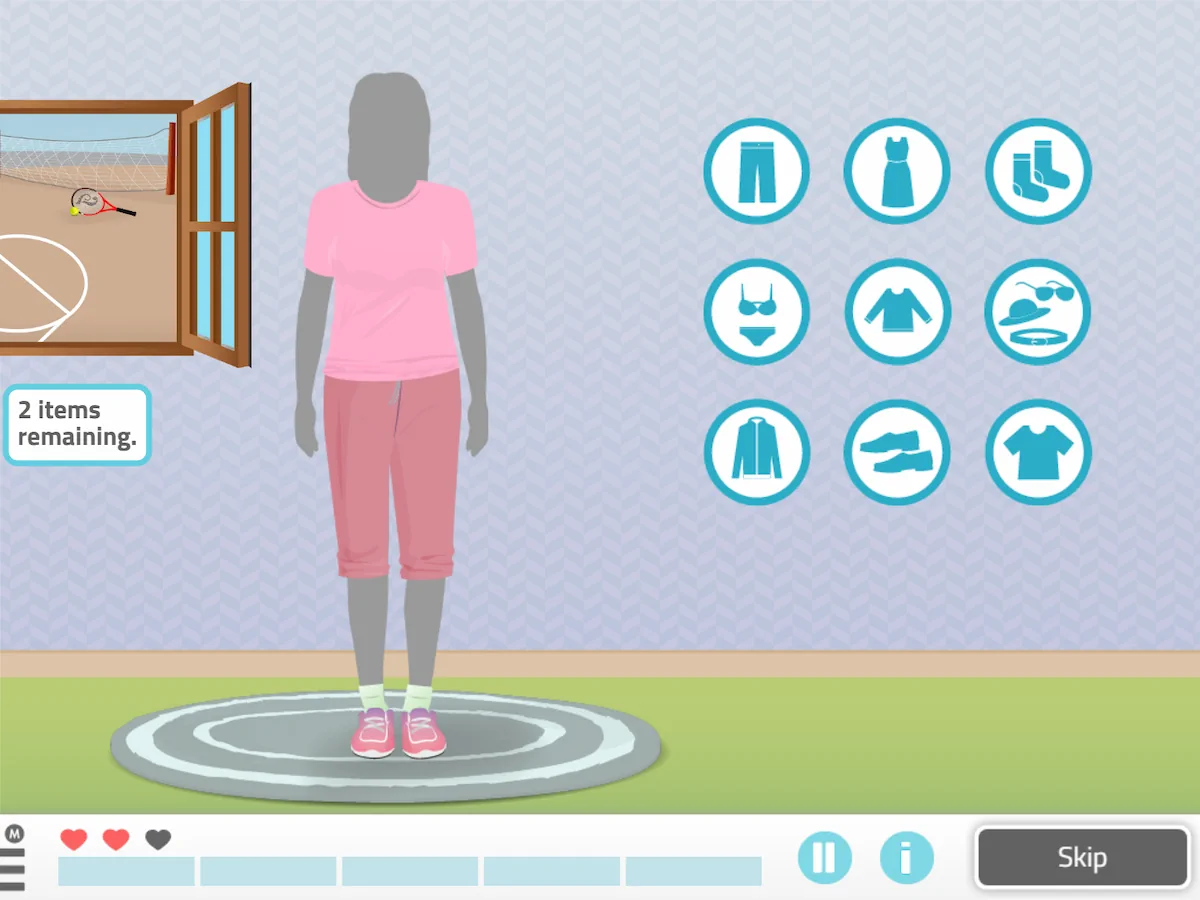
What does this activity work on?
This cognitive stimulation exercise works on the following cognitive functions:
- Decision making,
- body schema,
- planning,
- dressing.
Play by levels
There are 6 phases. At the easiest levels there are fewer orders and more prompts from the program to carry out the activity correctly, while at the more difficult levels prompts decrease and the dressing requirements are more complex.
Activity customization
In addition, you can customize the activity to adapt it to each user’s abilities.
Parameters
And, on the other hand, the parameters, where you can select the number of garments, the scenario, whether you want to include any type of distractor, the errors that can be made, the presentation of the garments, etc.
General aspects
You can adjust, on the one hand, general aspects such as the number of exercises, the maximum time, whether or not you want a visible stopwatch for the activity, modify the instructions for carrying out the activity, etc.
Adaptability
Finally, you can select whether you want the movement of the clothing items to be draggable or selectable with a single click to select the garment. Depending on the user’s functionality, one option or the other can be chosen.
6. Straighten Up the Kitchen
What does it consist of?
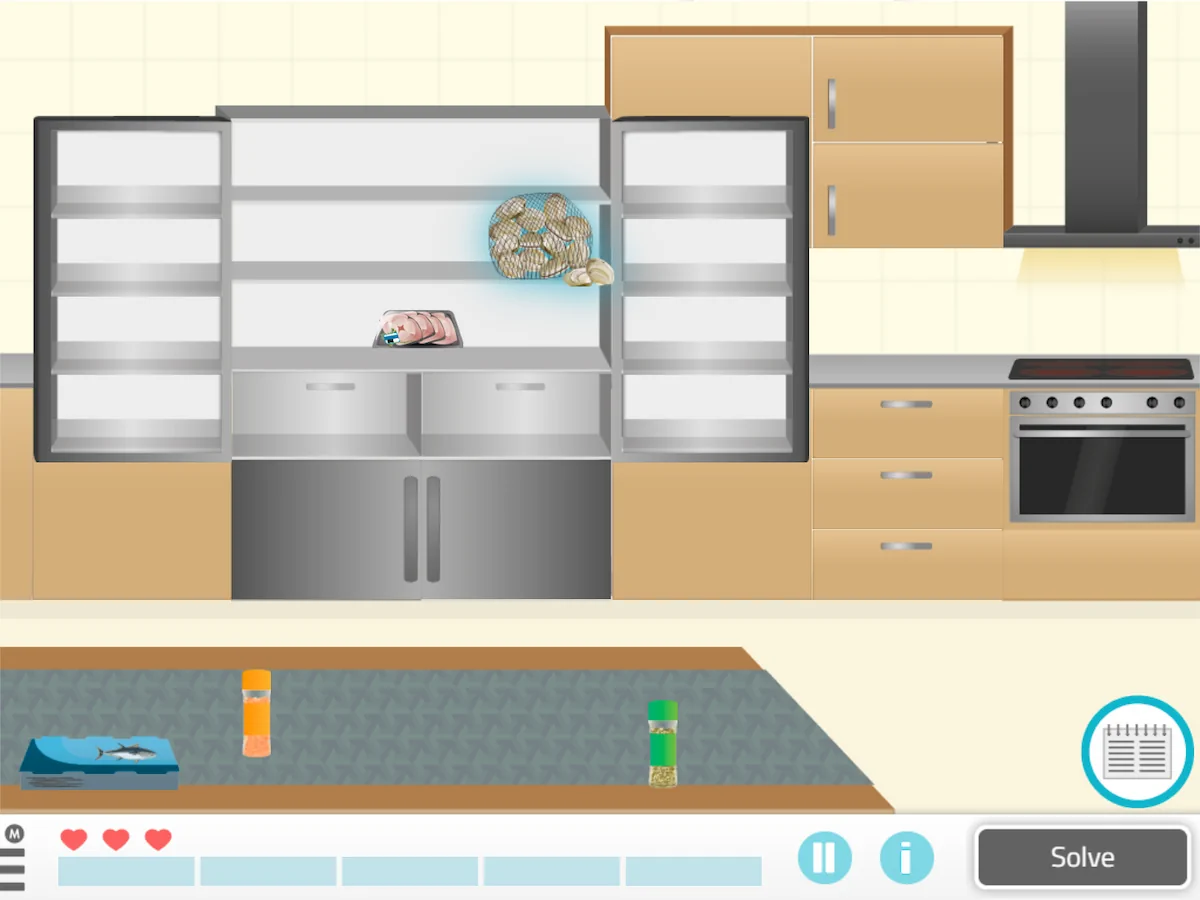
What does this activity work on?
Play by levels
Activity customization
Parameters
General aspects
7. Sound Counting
What does it consist of?
Counting is a game in which children must listen carefully and count the number of stimuli presented.
What does this activity work on?
This child activity with ecological validity works on sustained attention and processing speed.
Play by levels
Activity customization
You can customize this activity to adapt it to the individual needs and abilities of each child, being able to configure the general aspects and the parameters:
Parameters
On the one hand, the parameters, where you can select:
General aspects
8. Pick Up your Baggage
What does it consist of?
In this game you must select only the suitcases identical to the model from a set of moving luggage. Depending on the phase more suitcases will appear to recognize.
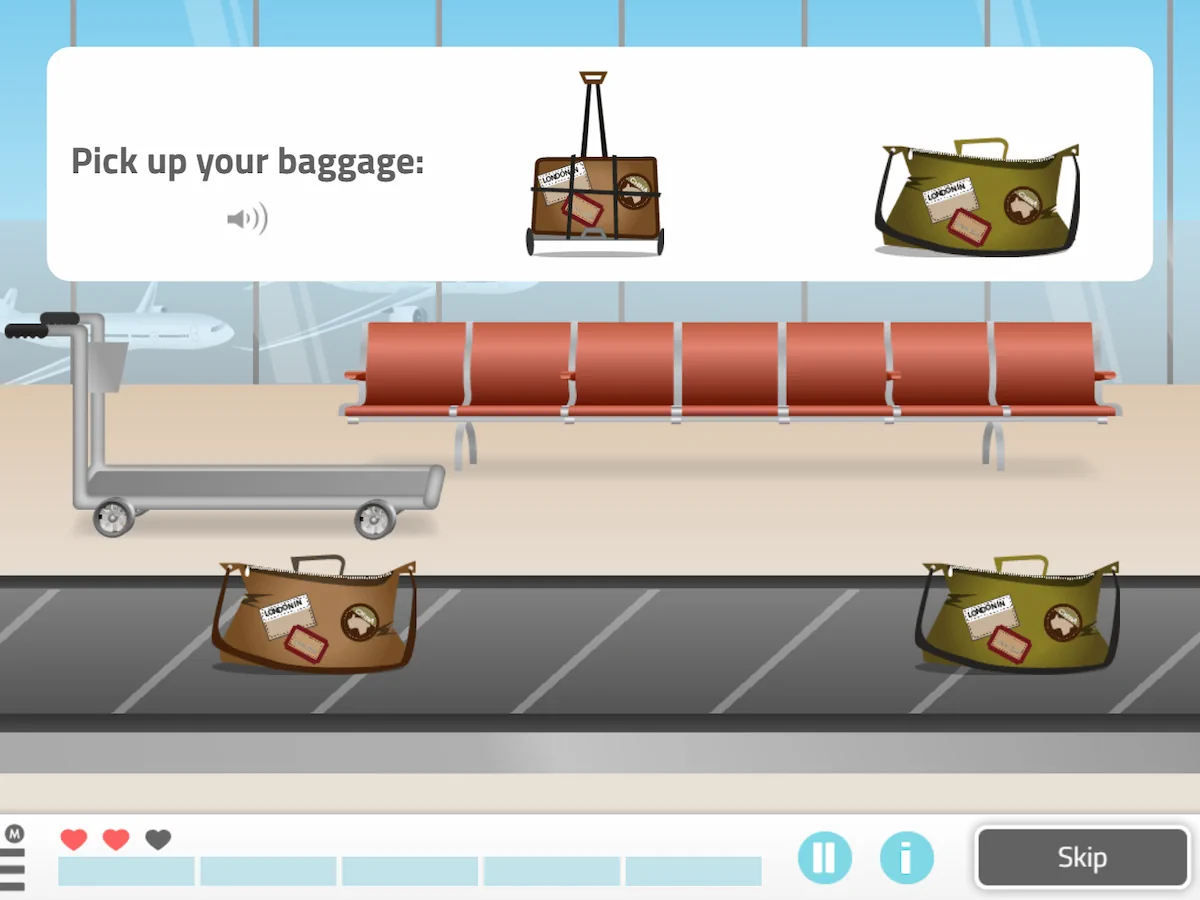
What does this activity work on?
In this adult exercise the following are worked on:
- Selective attention,
- sustained attention,
- working memory,
- processing speed
- leisure.
Play by levels
Activity customization
You can customize this activity to adapt it to the individual needs and abilities of each child, being able to configure the general aspects and the parameters:
Parameters
On the one hand, the parameters, where you can select:
General aspects
9. Differentiate numbers
What does it consist of?
It consists of choosing the dictated number among several options.
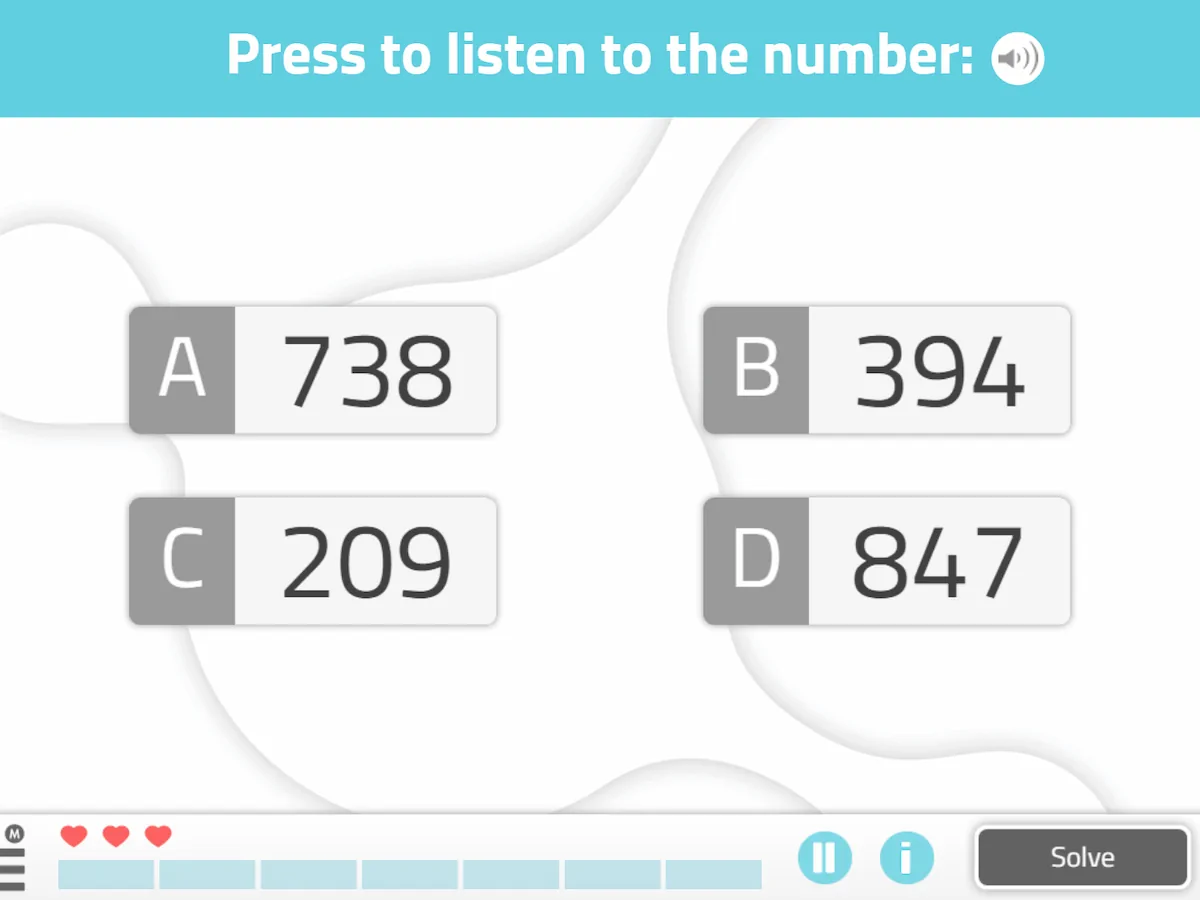
Play by levels
On the other hand, the activity What is the best thing to do? is organized into five difficulty levels: basic, easy, medium, hard and advanced.
Formato
This worksheet is available both in digital and in paper format.
10. Pack your Backpack
What does it consist of?
It is a game in which children have to prepare the backpack for school, selecting only the objects necessary for that day.
The objective of this daily living activity is that children do not forget anything. In addition, it also aims to prevent them from putting materials they do not need in their backpack and making it too heavy. The challenge is on!
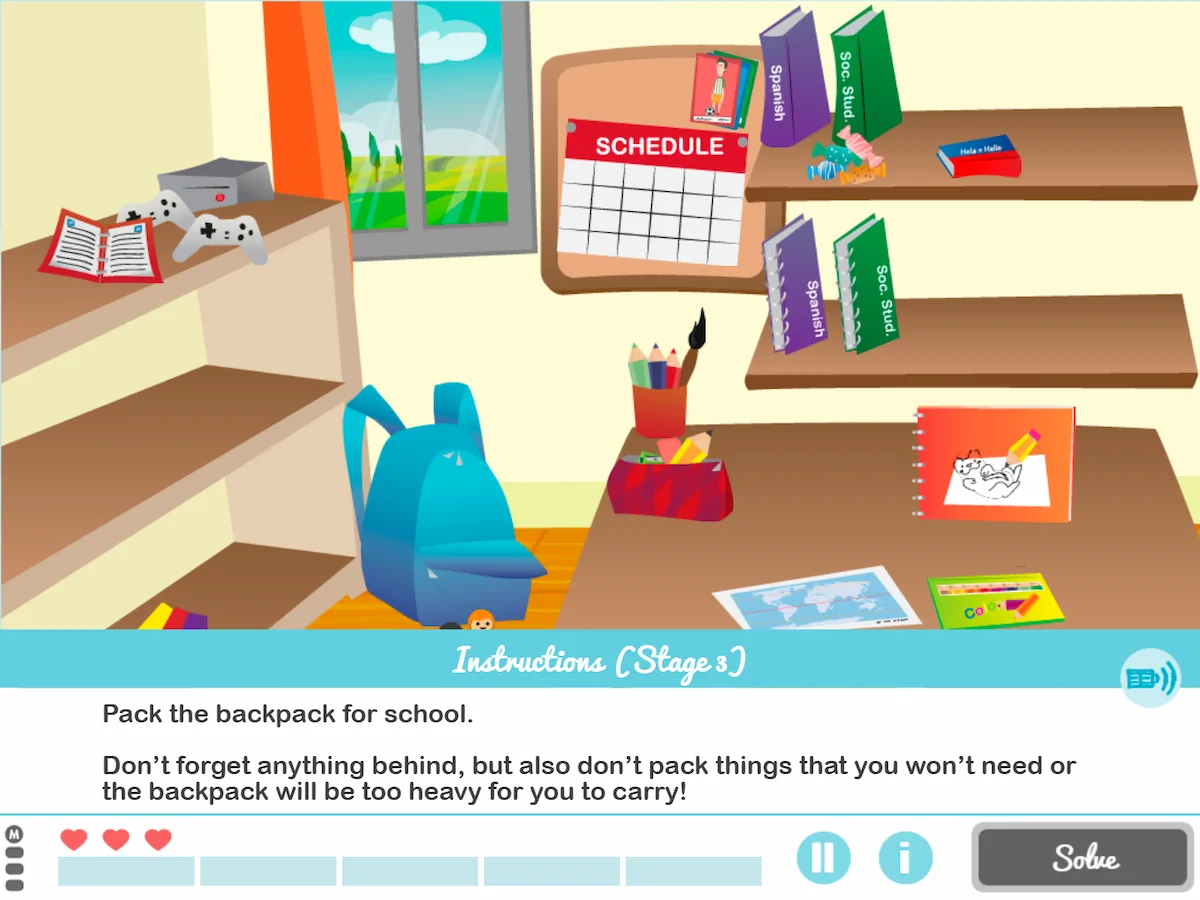
What does this activity work on?
This is a child activity to work on planning, that is, the child works on what to take based on the subjects they have each day. Also, selective attention is stimulated.
Play by levels
In addition, it is divided into six difficulty levels.
Activity customization
Likewise, in this ADL you can customize the game.
Parameters
- Number of subjects and type,
- cues: visible, hidden or none,
- distractors: related, unrelated, all or none,
- maximum errors.
General aspects
You can choose general features such as the number of exercises, the maximum time, whether or not you want a visible timer for the activity and an inactivity warning. Or you can modify the instructions.
These are just 10 ecologically valid exercises from NeuronUP. On the platform you can find many more. Request a free trial and try them with your users:
Bibliography
- Kvavilashvili, L., & Ellis, J. (2004). Ecological validity and twenty years of real-life/ laboratory controversy in memory research: A critical (and historical) review. History and Philosophy of Psychology , vol 6 , pp. 59-80.
- Tirapu Ustárroz, J., García Molina , A. & Roig Rovira, T. (2007). Validez ecológica en la exploración de las funciones ejecutivas. Anales de Psicología, 23(2) 289-299.
- Yantz, C. L., Johnson-Greene, D., Higginson, C., & Emmerson, L. (2010). Functional cooking skills and neuropsychological functioning in patients with stroke: an ecological validity study. Neuropsychological rehabilitation, 20(5), 725-738. doi:10.1080/09602011003765690
If you liked this about ecological validity in NeuronUP, you may also be interested in this information:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
Validez ecológica en NeuronUP: ejemplos





 Neuropsychological Sequelae of Childhood Cancer
Neuropsychological Sequelae of Childhood Cancer
Leave a Reply