Introduction
Cognitive rehabilitation exercises after a stroke are vital in the recovery process. Therefore, here we provide a series of rehabilitation exercises after a stroke ideal for the cognitive rehabilitation professional to work with the patient who has had a stroke.
Rehabilitation exercises after a stroke
Depending on the sequelae of the stroke, the patient should follow one rehabilitation treatment or another. Furthermore, it will always be the neuropsychologist or occupational therapist who decides.
Based on this observation, we propose 14 post-stroke rehabilitation exercises created by NeuronUP:
1. Objects, places and professionals
First, we bring you this exercise focused on improving the Place Orientation of the patient after a stroke.
What does it involve?
It involves matching various objects with the places where they are obtained and the professionals who handle them.
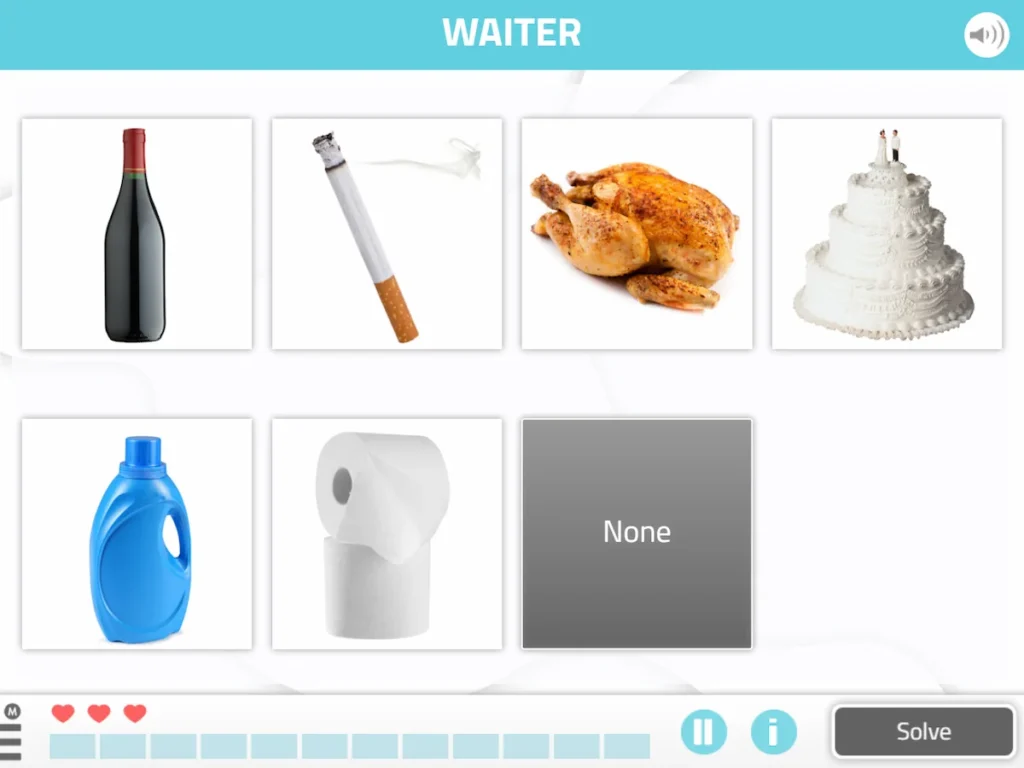
2. Find the Monument
The main aim of this exercise for stroke recovery is to improve attention. It consists of following the instructions as quickly as possible until finding the monument. Likewise, the cognitive functions it trains are the processing speed, sustained attention, working memory and planning.
What does it involve?
It involves following the instructions as quickly as possible until finding the monument.

What does this activity train?
Likewise, the cognitive functions it trains are processing speed, sustained attention, working memory and planning.

Subscribe
to our
Newsletter
3. Organize the Bookcase
What does it involve?
It consists of copying the position of the objects from the model. However, you must be careful when copying, since the shelf is mirrored, so you must copy the model in reverse
The model is on the right and the shelf to be arranged is on the left — would your patient who has had a stroke be able to arrange it correctly?

This is how it should look:
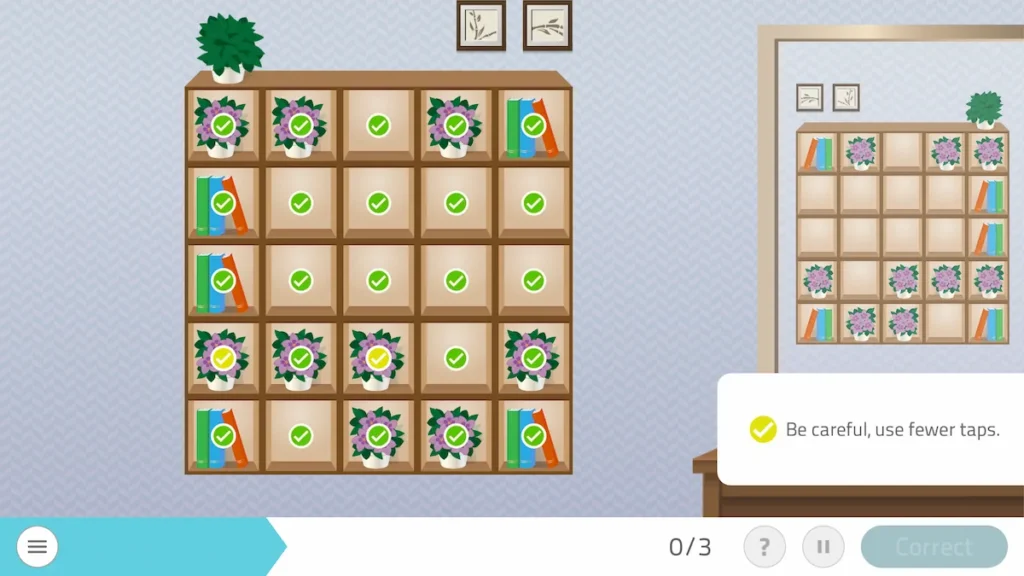
What does this activity train?
It is also designed to work on the recovery of sustained attention, selective attention, hemispatial neglect, spatial relations and processing speed.
4. Select items from a category
What does it involve?
It involves selecting a series of specific items from a group of stimuli, in this case the patient must point out all the furniture:
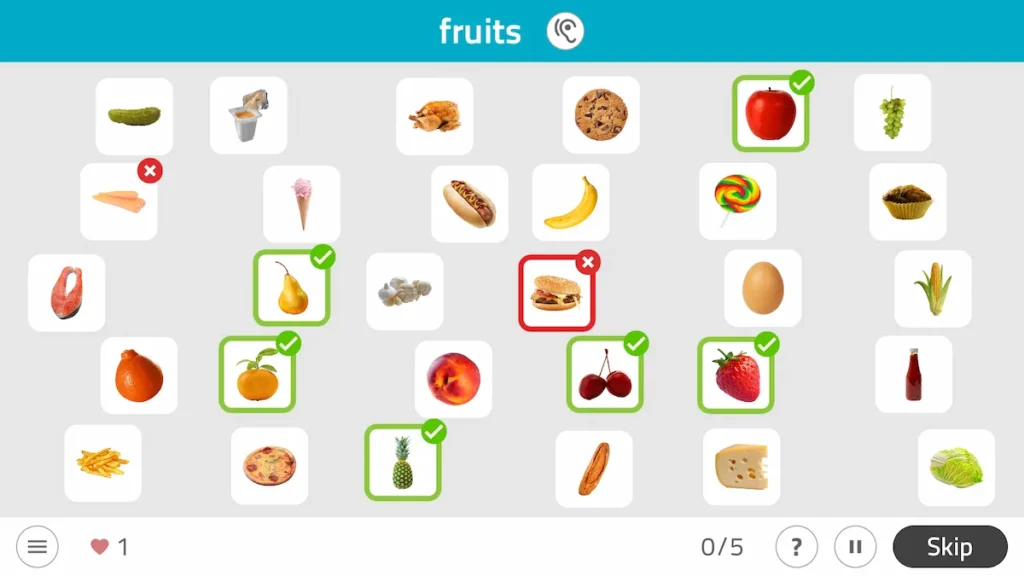
What does this activity train?
Indeed, this exercise is ideal for working on attention and semantic memory.
5. Maze with alternate instructions
What does it involve?
In this exercise you must traverse a labyrinth of figures following various instructions alternately. However, you must be careful, as there are a series of rules that must be followed.
Instructions to follow:
Get from the starting point to the target by alternating these rules to advance:
- Same letter, but different size
- Same size, but different letter
Also, you must take into account that you cannot move diagonally or repeat squares.
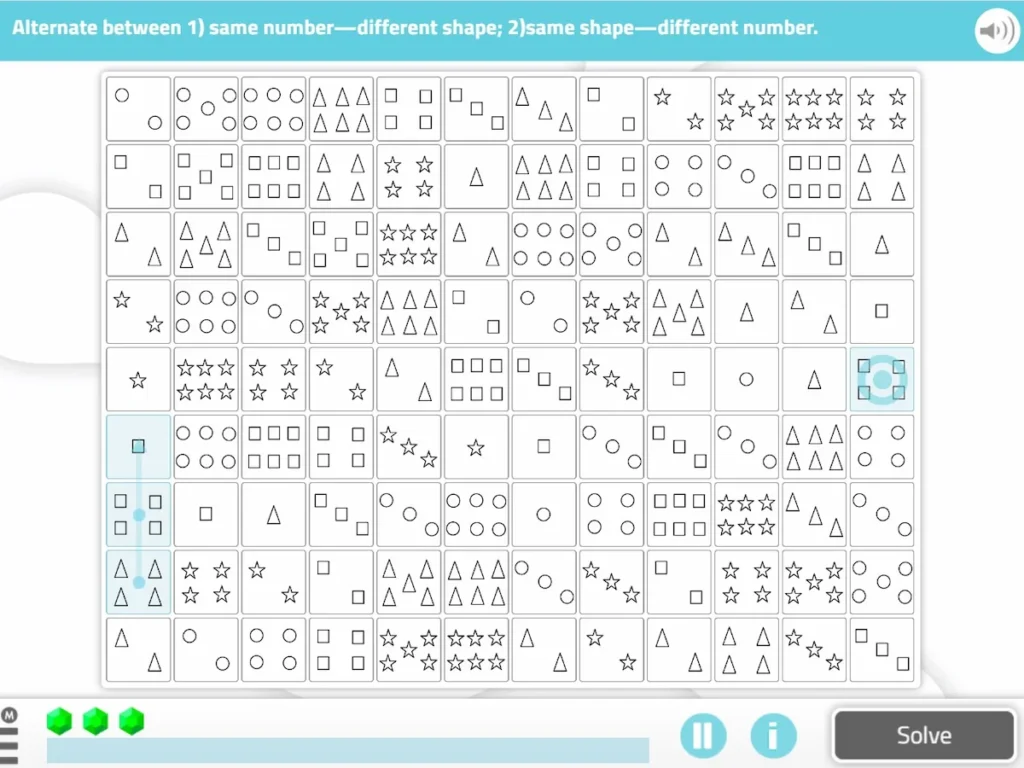
What does this activity train?
It trains alternating attention and selective attention.
6. Matching Words to Category
In addition to the activities already seen, another of the post-stroke rehabilitation exercises we present is Pairing items and category.
What does it involve?
It involves pairing elements with the category to which they belong.
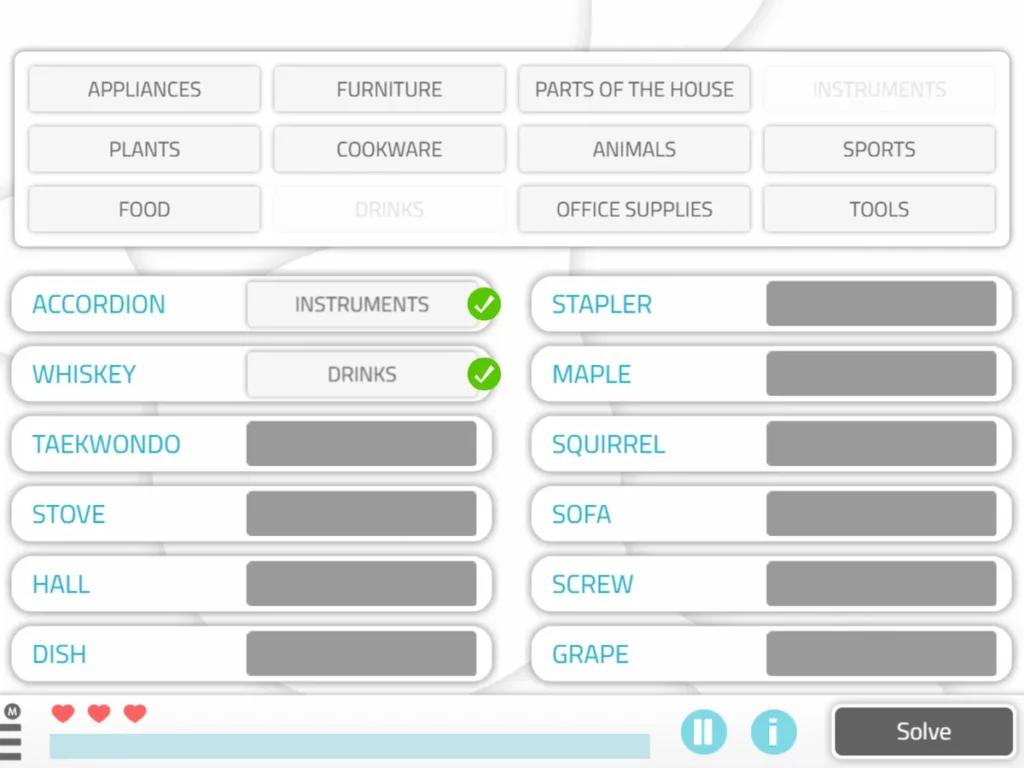
What does this activity train?
Likewise, it is aimed at working on semantic memory.
7. Match the Cards
What does it involve?
This activity consists of discovering pairs among a set of cards placed face down.
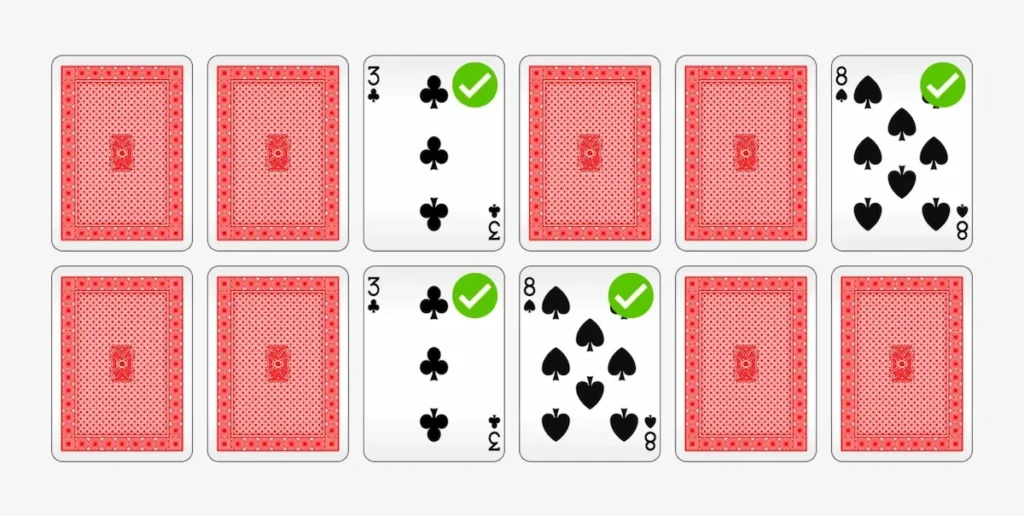
What does this activity train?
The cognitive functions trained are episodic memory, selective attention and working memory.
8. Form Sentences
If we are looking for activities for speech recovery after a stroke, this can be ideal, as it works on language.
What does it involve?
This activity is based on ordering the presented words to form coherent syntactic structures.
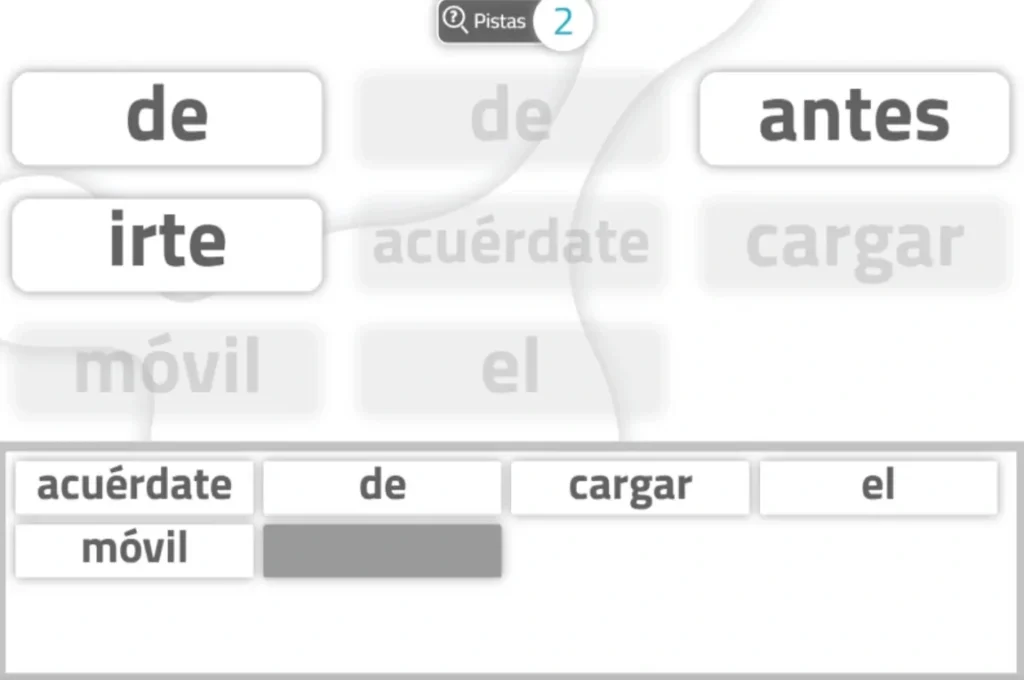
What does this activity train?
Specifically, this exercise trains expression, comprehension, flexibility, working memory and planning.
9. Hangman
What does it involve?
Similarly, another language-related activity is Hangman. The patient must try to guess the hidden words by choosing the letters that comprise them one by one.
Do you know which letter is missing?
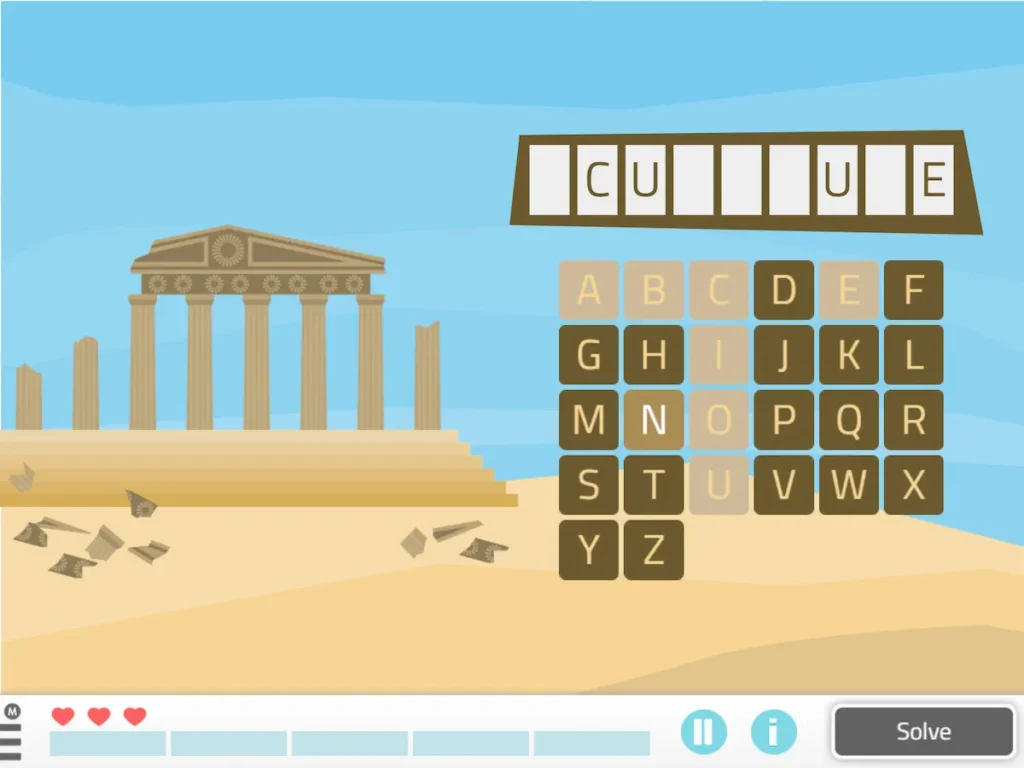
What does this activity train?
The patient works on vocabulary and working memory.
10. Task Sequencing (Picture-Only)
What does it involve?
In this NeuronUP worksheet you must put in order the different steps necessary to carry out an activity.
Order the steps to wash the face:
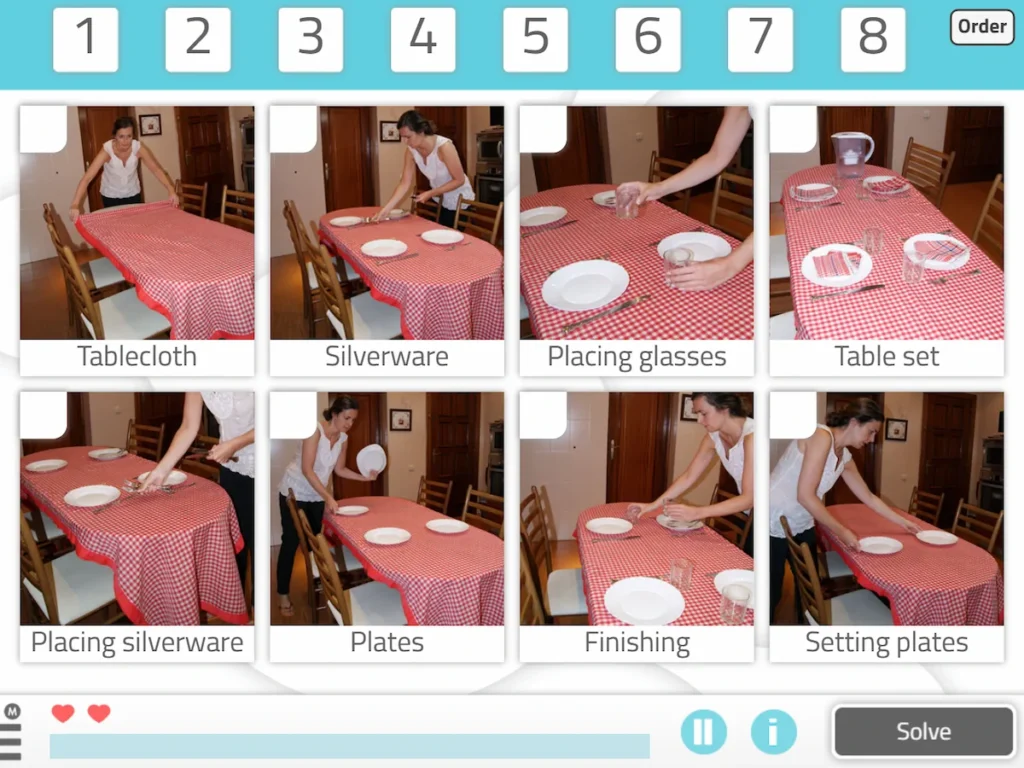
What does this activity train?
The cognitive functions trained with this exercise in the stroke recovery process are planning and comprehension. It also works on reasoning.
11. Half-hidden Objects
What does it involve?
After suffering a stroke the person must try to partially recognize Obscured Objects.
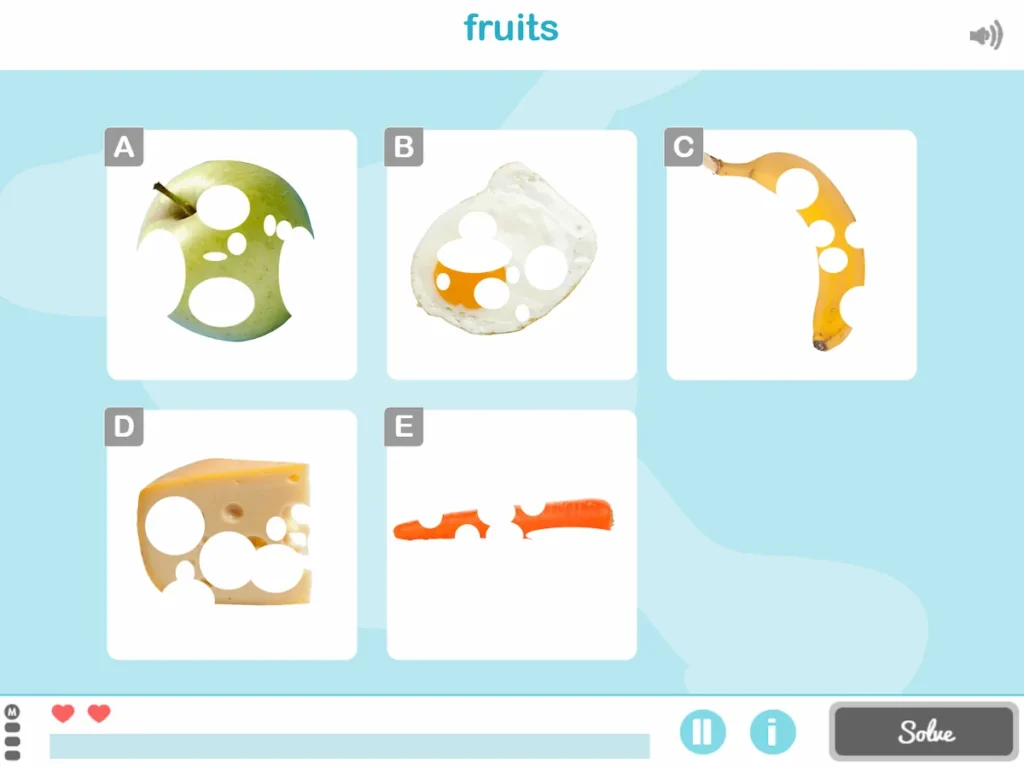
What does this activity train?
The patient works on visual gnosis and semantic memory.
12. Angles
What does it involve?
This activity consists of forming the indicated angle based on the given reference line.
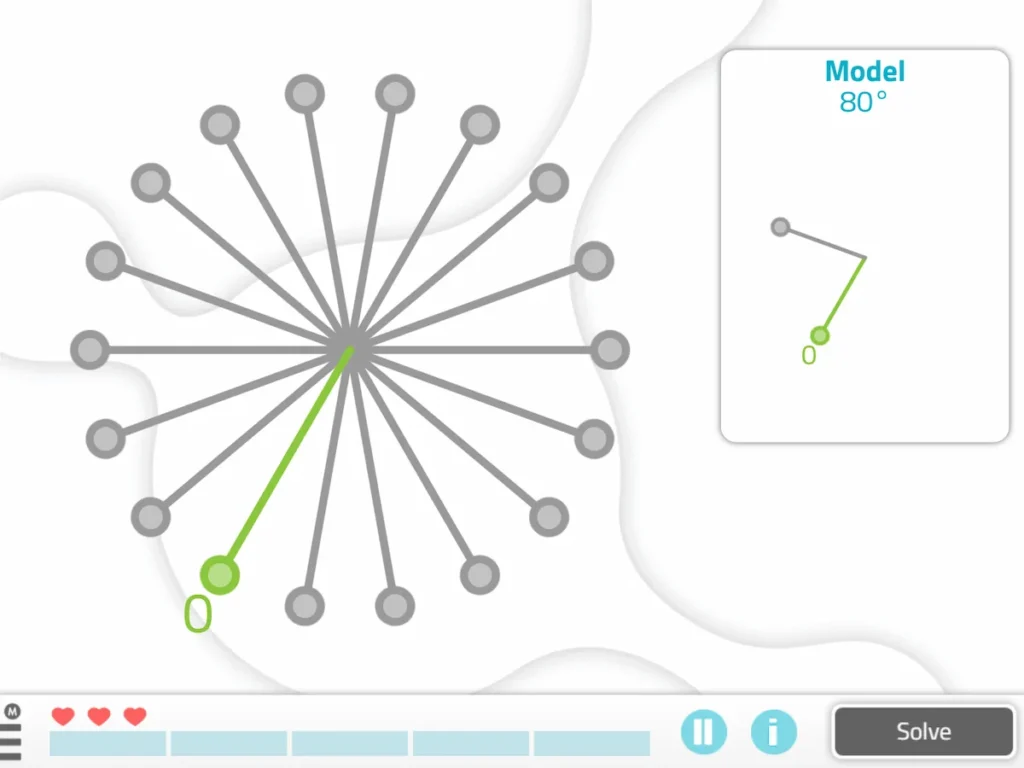
What does this activity train?
It works on spatial relations and also hemispatial neglect.
13. Emotion recognition
What does it involve?
Also, another of the post-stroke rehabilitation exercises we propose consists of recognizing the emotions shown and matching them with the terms that define them.

What does this activity train?
Likewise, this activity works on social cognition, vocabulary and reasoning.
14. Get Dressed
What does it involve?
To finish, we bring you a very useful daily living activity after a stroke. The patient must dress the silhouette appropriately, taking into account both the location and order in which each garment is put on and the type of situation.

What does this activity train?
Certainly, it works on procedural memory, body schema and ideational praxis. Likewise, it works on semantic memory and planning.
If you liked this article about rehabilitation exercises after a stroke, you may also be interested in the following information:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
14 ejercicios de rehabilitación después de un ictus





 The neuropsychological treatment at the IENSA center through NeuronUP
The neuropsychological treatment at the IENSA center through NeuronUP
Leave a Reply