Physiotherapist Ancor Vila González explains his therapeutic vision on physiotherapy and the dual-task in relation to his experience with NeuronUP.
Introduction
Physiotherapy can be defined as treatment through movement. While the dual-task is a therapeutic protocol where the objective is to enhance physical and mental performance by carrying out a physical exercise and a cognitive exercise simultaneously. The NeuronUP platform is the perfect tool to implement this pathway of simultaneous treatment.
My perspective on physiotherapy and the dual-task
During my therapies, results and therapeutic exercise form my axis of reflection. On the one hand, manual therapy helps me prepare the tissues to request their activation and foster synergy between them during directed physical activity. On the other hand, therapeutic exercise is a fundamental tool for the improvement of many symptoms and significantly influences the patient’s well-being.
This exercise program must be designed, programmed, periodized, supervised and evaluated by an accredited healthcare professional, in order to achieve the objectives set during assessment.
At Vila Fisioterapia we state and apply the premise that the patient should be the main character during the time the therapeutic accompaniment lasts and beyond. For this reason, they must understand their problems, the causes and what behavior and attitude are necessary for the change towards well-being and health.
From my experience, promoting patient empowerment is one of the levers of success to be able to achieve the set goals.
Physical Exercise and cognitive performance
Skeletal muscle behaves like an endocrine organ. According to certain authors, it has the ability to release protein substances with hormonal action called myokines. These proteins produce their effect on tissues sensitive to them and these target regions can be located both proximally and in the periphery.
Focusing in particular, the Factor BDFN (Brain-Derived Factor Neurotrophic) is one of these proteins whose target tissue is the central nervous system. This hormone is currently identified as the hormone that improves cognitive performance and promotes neuroplasticity within a training established from specific elements.
Dual-task
According to the scientific literature on the subject, it is a therapeutic element that improves both the individual’s physical performance and cognitive capacity. According to some authors, therapeutic exercise under certain conditions favors the individual’s cognitive capacity.
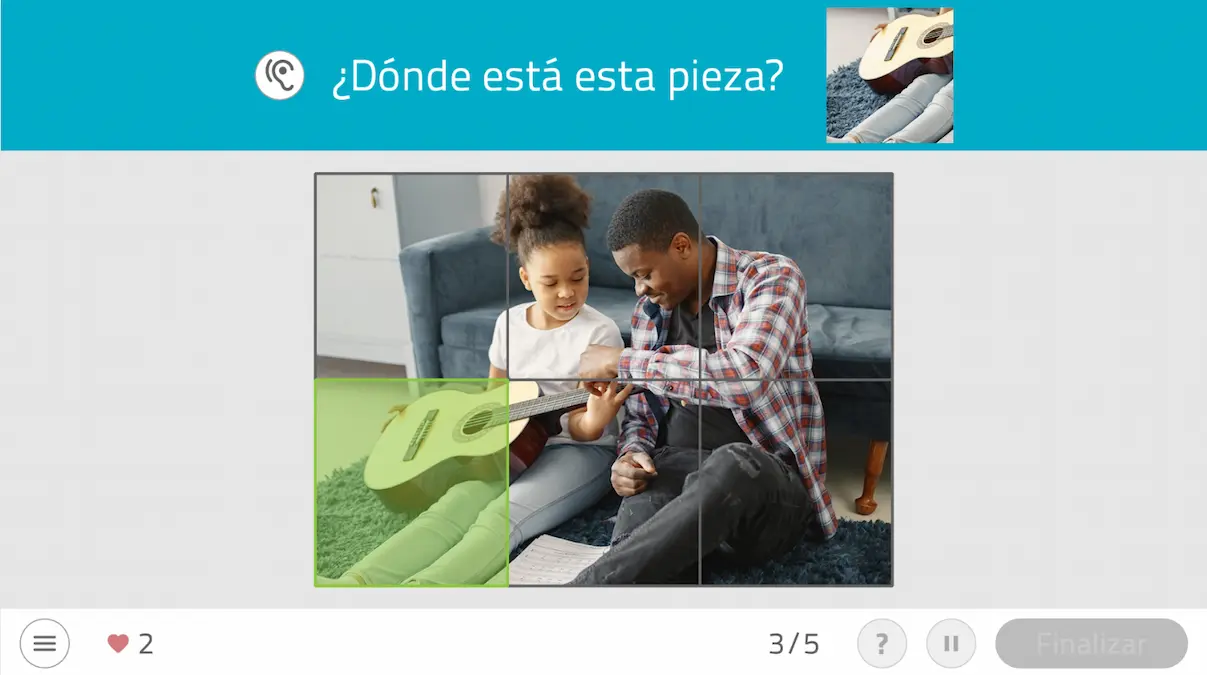
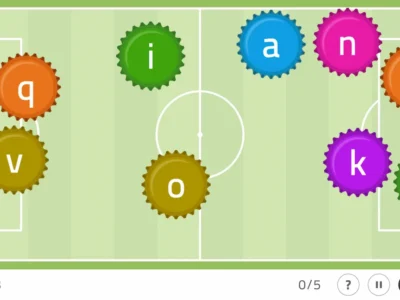
Following this premise, we propose to the patient a physical stimulus, generally based on proprioception exercises and a simple cognitive activity. Depending on each patient’s personal capacities, the proposed exercises, both physical and mental, evolve in their complexity.
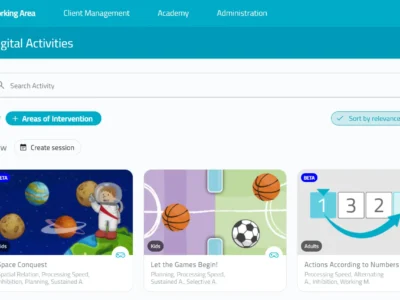
Use of NeuronUP in physiotherapy and the dual-task
NeuronUP has generated a leap toward the digitization of my therapies. Currently, and thanks to this software, I can propose a directed physical activity and a digital cognitive task at the same time, both in the clinic and at home.
It also livens up therapies and promotes patient adherence to the treatment. Likewise, NeuronUP’s ergonomics allow for the personalization of exercises for each patient and the motivating stimuli received increase the patient’s willingness to change.
Conclusion
It is well known that continuity and adherence are important elements to reach objectives and that fun and variability of exercises allow us to achieve the set goals.
NeuronUP likewise promotes patient automation. Since, through NeuronUP2GO, NeuronUP’s at-home sessions, the individual can carry out their exercises both physical and cognitive at home. This allows us to evaluate the person’s autonomy, their engagement and the physical and cognitive performance of the therapies.
In conclusion, I want to emphasize the positive and accelerating effect of implementing our physical therapies with elements of cognitive training.
Furthermore, this promotes adherence, autonomy, performance and the person’s self-esteem.
References
- Exercise-Induced Neuroplasticity: A Mechanistic Model and Prospects for Promoting Plasticity. El-Sayes J, Harasym D, Turco CV, Locke MB, Nelson AJ. Neuroscientist. 2019 Feb;25(1):65-85. doi: 10.1177/1073858418771538. Epub 2018 Apr 21.
- Relationships between components of physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, cardiac autonomic health, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Ramsbottom R, Currie J, Gilder M. J Sports Sci. 2010 Jun;28(8):843-9. doi: 10.1080/02640411003702686.
- Crossfit training changes brain-derived neurotrophic factor and irisin levels at rest, after wingate and progressive tests, and improves aerobic capacity and body composition of young physically active men and women. Murawska-Cialowicz E, Wojna J, Zuwala-Jagiello J. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;66(6):811-21.
- Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function. Gómez-Pinilla F. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008 Jul;9(7):568-78. doi: 10.1038/nrn2421.
- Myokines: a descriptive review. Barbalho SM, Prado Neto EV, De Alvares Goulart R, Bechara MD, Baisi Chagas EF, Audi M, Guissoni Campos LM, Landgraf Guiger E, Buchaim RL, Buchaim DV, Cressoni Araujo A. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020 Dec;60(12):1583-1590. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.20.10884-3. Epub 2020 Jun 23.
- The influence of exercise on cognitive abilities. Gomez-Pinilla F, Hillman C. Compr Physiol. 2013 Jan;3(1):403-28. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c110063.
If you liked this post about Physiotherapy and dual-task: therapeutic exercise with NeuronUP, we recommend you take a look at these posts:
“This article has been translated. Link to the original article in Spanish:”
Fisioterapia y doble tarea: el ejercicio terapéutico con NeuronUP




 Intervention with NeuronUP in people with Down syndrome
Intervention with NeuronUP in people with Down syndrome
Leave a Reply